VPS vs VPN: Which One Do You Need?
Despite having similar names, a VPN (Virtual Private Network) and a VPS (Virtual Private Server) are two completely different concepts. Indeed, they sometimes use the same technology, and, broadly speaking, they serve a similar purpose – allowing users to access specific resources on the internet.
However, there are some fundamental differences in how they work and fit into our everyday lives. Today, we’ll explore them in more detail.
What is a VPN?
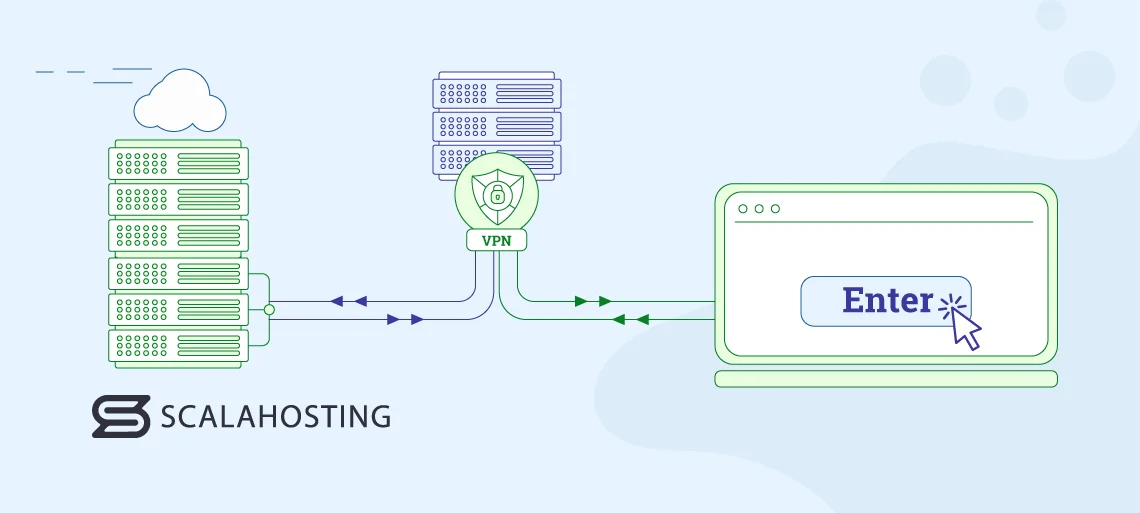
The goal of a VPN is to protect the user’s privacy by redirecting their internet traffic. To find out how it does that, we need to understand what happens when you try to open a website or watch a movie on Netflix.
As soon as you click Enter, your device sends a request to the server hosting the content you want to access. In addition to the URL page you want to open or the movie name you want to find, the request contains a ton of potentially identifiable information, including the type of device you’re using and the IP address of your local network. The data is visible not only to the destination server but also to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and to anyone else who might be eavesdropping on your connection.
If you use a virtual private network, your request first passes through a server owned and operated by your VPN provider before being directed to the destination server. Thus, it appears that the VPN server, and not you, is trying to open the website or watch the movie.
Sounds simple, right? Well, there’s a bit more to it than that.
How does a VPN work?
Based on the information above, those of you who have been around computers long enough may say that using a VPN is the same as having a proxy server. Indeed, a proxy uses the same basic mechanism to mask your IP address. However, a couple of other aspects of a VPN’s operation make it a completely different solution.
VPN works on a device level
When you use a proxy, you configure specific applications to work with it. For example, if you open your browser’s settings, you’ll find a section that lets you enter the address of your proxy server and reroute the traffic through it. The websites you visit won’t be able to see your IP, but the rest of the apps on your device continue to work as usual.
By contrast, you need to install a client on your computer or smartphone to use a VPN. Once enabled, it will reroute all your traffic, regardless of the application, through the virtual private network. Everything you do online, be it browsing websites, watching videos, or downloading software, passes through your VPN.
VPN encrypts your data
The only privacy-protection benefit of a proxy is the fact that the owner of the resource you’re trying to access has no idea what your IP is. However, your internet service provider (ISP) can still see what you’re doing. And if your ISP knows your actions – other people may be able to get their hands on that information as well.
The idea of a virtual private network is to prevent this.
Before any traffic passes through your virtual network, your VPN software establishes an encrypted connection between your device and the VPN server. Every bit of information is scrambled before it leaves your computer or phone, meaning internet service providers, the government, and any hackers trying to snoop around will have absolutely no idea what you’re doing.
Your ISP may be able to see that you’re communicating with a VPN server, which could attract unwanted attention. However, providers are now implementing techniques to disguise your VPN connection as standard HTTPS traffic. Even if it is visible that you’re using a VPN, your actual activity remains protected.
Once your request reaches the VPN server, it is decrypted and sent to its intended destination. To ensure maximum protection, the VPN provider also encrypts the responses before sending them back to you.
In other words, a VPN is a service designed to prevent anyone from seeing and examining your online activity.
Why use a VPN?
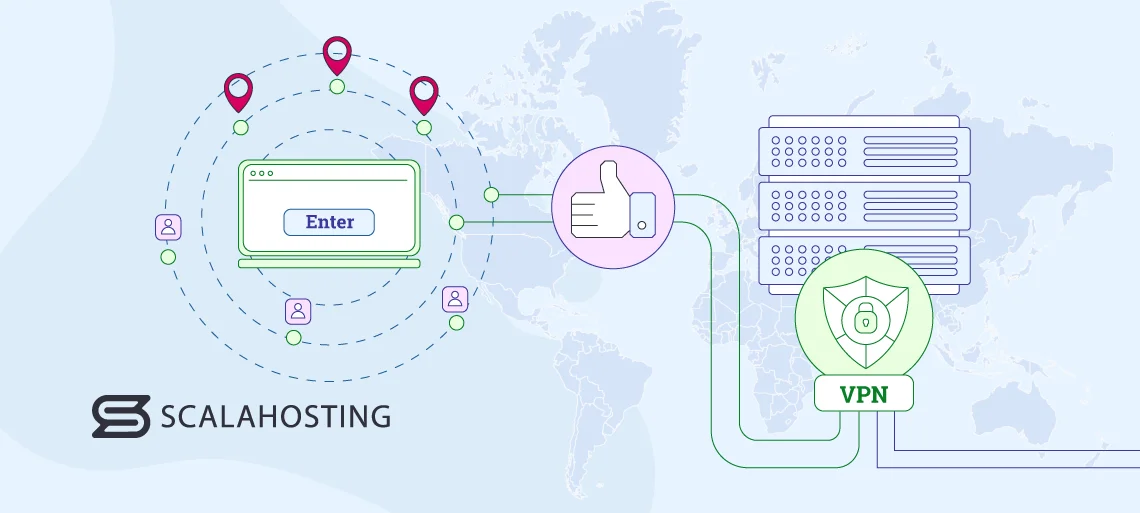
Reading all this, you may think that a VPN is aimed at people who have something to hide. That’s not strictly the case. In fact, there are many reasons for using a VPN service.
Let’s explore some of them:
- Private Browsing
Data collection companies go to great lengths to learn as much as possible about every single internet user. Using trackers and other resources, they try to gather information regarding your browsing habits and interests.
Although these companies must stick to specific rules and regulations (which they don’t always do), their business is not illegal. Often, the collected data is used for genuinely useful purposes, as well.
However, you have little control over what sort of information they gather about you, and you don’t know where it will end up. Furthermore, having someone watch you all the time is intrusive, and the data can sometimes end up on malicious websites or be used for various nefarious purposes.
By hiding behind a VPN server, you can severely limit the volume of data companies can collect about you. Because they don’t know your IP address, tracking your browsing history is a challenge.
- Building a secure corporate network
It’s the 21st century, and working remotely is standard practice for many. This means accessing corporate data and using company resources on the move. Using remote access VPN solutions, businesses can ensure this happens safely.
- Accessing streaming content that is unavailable in your geographical region
YouTube, Netflix, and Spotify are all global platforms, but their content isn’t uniformly available worldwide. Music artists, songs, movies, videos, and even podcasts can be geo-locked for various reasons, ranging from licensing contracts to government restrictions.
The only way to access this content without moving house is to use a VPN with servers outside your country. Most providers have hardware in multiple geographical regions, and you can often pick which one you’d like to use every time you power up the VPN client.
- Avoiding censorship
In addition to content, some governments also restrict the use of websites, applications, and online services to stop the free flow of information and shield their propaganda efforts.
A VPN service allows you to use the IP of a server located in a different country, meaning you can access restricted resources. Crucially, you can do it without your ISP knowing about it.
- Spoofing your location
Combining a foreign IP and a secure connection allows you to effectively spoof your location and prevent websites and online services from knowing where you are. You may want to do that for various reasons.
- Comparing prices in different geographical regions
Global ecommerce stores often have different pricing policies for different geographical regions. For example, if a specific product costs $100 in the US, it could be the equivalent of $150 elsewhere. Using a VPN, you can “travel” around the world, compare prices for the same item, and get the best deal.
- Use public Wi-Fi safely
As a general rule, it’s best to avoid Wi-Fi networks that are not protected by a password. Even if there is some form of protection, public networks such as the ones available in cafes and airports should be approached with extreme caution, as you never know who set up the router, what form of protection it uses, and how many people may have tried to break it.
The use of a VPN eliminates many of the risks. Any data that leaves your device is encrypted, so even if someone can sniff through it, they won’t be able to find anything useful.
What is a VPS?
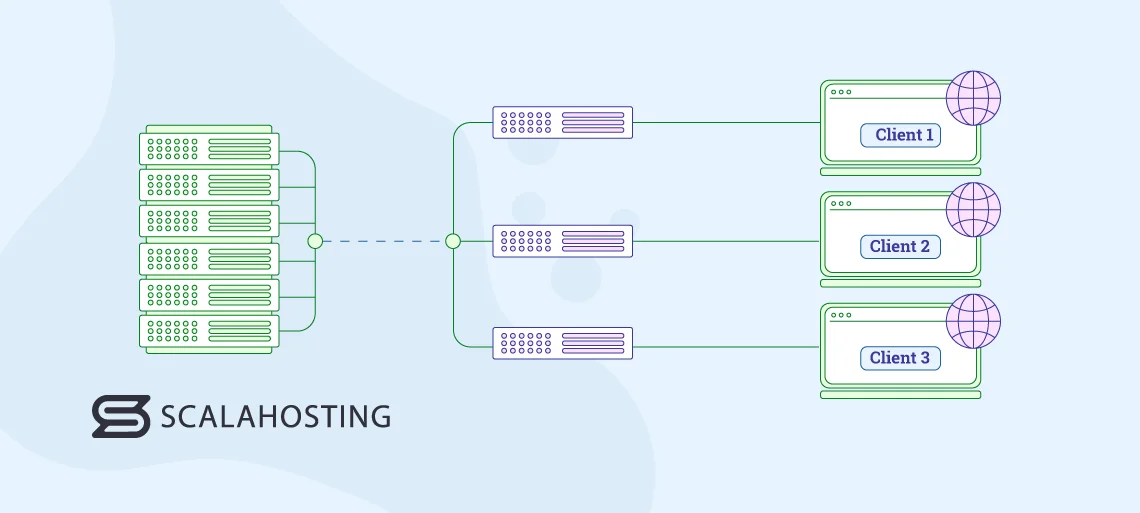
A VPS is a virtual machine. Its primary purpose is to provide users with an isolated environment that acts and has the exact same characteristics as a standalone physical server. In other words, like a physical machine, a VPS has its own operating system, IP, and hardware resources.
The difference is that you don’t actually have a dedicated physical server. Instead, the VPS provider takes a physical machine and installs a hypervisor – software that allows multiple operating systems to run concurrently on the same hardware. Thanks to it, a VPS hosting company can set up multiple smaller virtual servers on the same physical machine.
Setups can vary. Traditionally, each physical dedicated server would have its own set of VPSs. However, although multiple virtual machines are situated on the same server, they don’t share system resources. Each VPS is allocated a predetermined slice of processing power, memory, and storage that is available and reserved for it. The guaranteed resources make the performance more consistent and predictable compared to other services. However, a few recent technological advancements have led to the development of a more modern setup with quite a few advantages.
Using virtualization technology, providers can now use multiple physical servers to create what’s known as a cloud. The physical machines are clustered to provide an enormous pool of hardware resources that VPSs can tap into.
Your VPS will still have its own guaranteed resources, but because it’s deployed in a cloud environment, the configuration can be changed much more easily. Furthermore, because there’s no limit on how big the cloud can be, your virtual machine can be scaled pretty much infinitely.
The second significant advantage of using a cloud server is its reliability. A traditional VPS depends on its underlying physical machine. If it fails, all VPSs deployed on it go down with it.
By contrast, cloud servers rely on multiple physical devices working together. If one of the nodes in the cloud goes down, the rest will automatically take up the slack and ensure your VPS remains online at all times.
How does a VPS work?
Before you can start using your VPS, you must configure it. The steps and available options differ from hosting provider to hosting provider, but the factors you need to consider are the same:
- Server location
VPS hosting providers often give you a choice of data centers for your virtual server. Choose the one closest to your target audience.
- Operating system
The choice of an operating system should be dictated by how you plan to use the server. For example, if you want to set up a Forex trading platform, you’ll need a Windows server. For website hosting, you’ll most likely prefer a Linux distribution.
- CPU cores
Your hosting provider splits the available hardware CPU into cores, which are distributed among the virtual machines. The more cores, the more processing power.
- RAM
The server’s RAM is a temporary data storage facility that enables applications to respond to instructions more quickly. More memory means more stable and responsive software.
With the VPS configured and deployed, it’s time to log in and use it.
How you proceed depends on the server’s operating system and the installed software. If your VPS runs on Windows, for example, you’ll need to use the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) or Microsoft’s Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT).
With a Linux server, you can connect to the server using secure shell (SSH) and manage files and folders through an FTP client. Often, you’ll have a control panel as well.
A web hosting control panel is a GUI-based server management system that integrates all the tools you need to launch and run the projects hosted on your VPS. It also allows you to monitor resource usage and server load. Here, for example, is how SPanel, ScalaHosting’s management solution, tells you how healthy your VPS is.
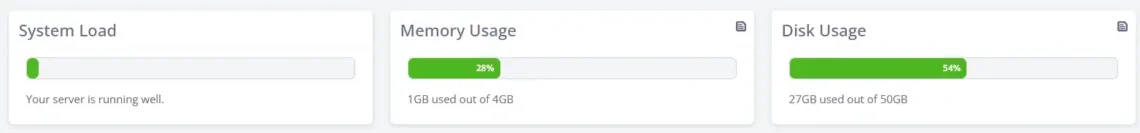
If the graphs above start filling up, you’re reaching the capacity of your virtual server and need to upgrade it. This is about as easy as it gets.
Thanks to the virtualization technology powering your server, you can add resources with as little as a couple of clicks. With traditional VPS services, you usually have a few configurations to choose from. For example, if your server currently has 2 CPU cores, 2GB of RAM, and 20GB of storage, and you need more power, you have to upgrade to the next plan, which has 4 cores, 4GB of RAM, and 40GB of storage space.
Cloud services are much more flexible. If your CPU usage is rising, but you don’t need additional storage or memory, a cloud VPS will allow you to add one more core without changing the RAM or SSD capacity. As a result, you’ll never need to pay for resources you don’t use.
What is a VPS Used for?
Because it’s effectively a standalone machine, there’s no limit on the number of applications you can find for your virtual server. Let’s have a look at some of them:
- Using a VPS to host websites
Web hosting companies have been trying to optimize the utilization of physical hardware for ages, and virtualization technology has allowed them to create a unique industry-wide solution that combines flexibility, performance, and cost-efficiency.
- As an email server
Creating and managing your inboxes on a virtual server will help you build secure, reliable communication with your business partners.
- As a backup server
You hear people say that regular backups are crucial. However, few discuss the importance of backup storage. By putting your backup on a reliable virtual server, you can be sure they will be readily available and easy to restore.
- As a storage and file sharing solution
Any files you store on your VPS are accessible at all times from anywhere in the world. This could come in handy if you need some data to save and share securely.
- As a gaming server
If it’s powerful enough, your VPS will have no problems hosting online multiplayer games.
- As part of a VPN
Your VPS has a dedicated IP and acts as a standalone machine, so there’s nothing stopping it from being a part of your virtual private network.
- As part of a virtual private cloud
If you have the technical skills, you can build your own private cloud environment using multiple VPS servers.
- Reselling your web hosting service
You can create multiple accounts on your virtual private server and rent them out to other website owners. The virtual server is also a good fit for developers and agencies who want to offer hosting alongside their services.
Why use a VPS?
A quick Google search returns quite a few results that say a VPS is suitable for ecommerce projects and websites with more significant traffic levels. This isn’t wrong, but it presents the virtual private server as a mere alternative to shared hosting. And it’s so much more than that.
A VPS provides an answer to quite a few questions and has advantages that make it the best candidate in a broad range of scenarios. Here’s a rundown of its most significant benefits.
- Complete control over the server
Before deploying the virtual server, you choose its hardware configuration. After it’s up and running, you access its operating system and do whatever you want. Some Linux VPS services offer root access, allowing you to fully customize the environment.
- Scalability
A virtual private server lets you start your project with a small, budget-friendly solution and build up from there. Upgrades are practically seamless and require no expensive migrations or downtime. If your virtual server is deployed on a properly configured cloud infrastructure, the sky is the limit when it comes to hardware resources.
- Versatility
A virtual server is far from a run-of-the-mill web hosting service. Because you have an entire server to yourself, you’re free to use it in a number of different scenarios. Moreover, the combination of powerful hardware and a completely isolated environment allows you to use it for two applications simultaneously. For example, with the right tools, you can set up your staging and production sites on the same server.
- Security
The isolated environment of your VPS protects your project from quite a few outside risks. For example, if you share server resources with other users, a DDoS campaign launched against one of your neighbors will inevitably affect you as well. In addition, if another person on the shared physical server starts sending spam, the server’s IP will be blocked, and your emails will start landing in your recipients’ spam folders. With a VPS, you’re the virtual server’s sole owner, so this isn’t a problem.
VPN vs. VPS – Do They Compare?
VPSs and VPNs are very different, but this doesn’t mean they can’t be used in conjunction. For example, you can configure your VPS to be accessible only via a VPN, which prevents outside people from tampering with your project.
You can also use multiple virtual servers to build your own custom-made VPN. You can deploy them in the most suitable data centers and implement your own encryption mechanisms and security systems.
The great thing about both services is that they’re suitable for users of all backgrounds.
Modern VPN client applications have an intuitive graphical user interface, as do the most popular control panels offered by VPS services. In other words, you don’t need lots of experience to take advantage of a VPS or a VPN.
At the same time, with enough technical skills and knowledge, you can harness the true power of these services.
ScalaHosting and VPS Hosting
ScalaHosting’s primary focus has always been on providing website owners with the environment they need to launch their projects and grow them into successful online businesses.
Our experience has taught us that a virtual private server is the perfect platform for the job, which is why VPS hosting is at the center of our portfolio of services.
Our managed VPS solutions are deployed in a proper cloud environment, meaning you have a high degree of flexibility and pretty much infinite customization options. You can specify your server’s hardware configuration to your exact requirements and upgrade individual components as and when you need to.
Because the service is fully managed, our technical experts will be responsible for your VPS’s initial configuration and ongoing maintenance tasks. Meanwhile, you can focus on launching and growing your website.
You’ll do it via SPanel – a server management platform built by ScalaHosting and aimed at providing you with everything you need to build a successful website. You have a graphical user interface with tools for installing applications, setting up email and FTP accounts, managing files, databases, subdomains, and pretty much anything else you may need to run a website.
Don’t hesitate to contact us if you need any additional information.

Conclusion
Given the enormous volume of technical terms and jargon users encounter every day, it is easy to see how they may struggle to distinguish between a virtual private server and a virtual private network.
The good news is that information on what the two types of services do is readily available, so after a few minutes of research, you should have no problems determining whether you need a VPS, a VPN, or both.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is a VPN safe to use?
A: The thing you need to bear in mind when choosing a VPN provider is that all your internet traffic will pass through its servers. You trust the company with quite a lot of potentially sensitive data, so it’s imperative that you pick a reputable provider.
Q: Which VPS hosting is best?
A: Quite a few factors should influence your choice of a VPS hosting solution. Your project’s hardware requirements are an obvious consideration, but things like the control panel and the server’s technical configuration should also be borne in mind. As a rule of thumb, you should go for a managed VPS service if you’re looking to build an online project with the help of your provider and a self-managed VPS if you are more experienced and need full control over the server..
Q: Can I use a VPS as a VPN?
A: Yes, you can use a VPS as a virtual private network. Every VPS has a dedicated IP, and there’s nothing to stop you from redirecting your internet traffic through it. A typical virtual server also has enough computing power to encrypt every bit of information that passes through it. Compared to commercial VPN services, the downside is that you’ll have to set everything up yourself.
What is a VPS – Everything you need to know!