How to Install an SSL Certificate
SSL certificates help keep website visitors safer. The best part of all is that only website owners need to install SSL certificates – a set-it-and-forget-it task. Yet even something as straightforward as this can be rather complex due to various certificate types.
SSL certificates remain one of the fastest ways of increasing website security and inspiring customer trust- sometimes, at no cost. To learn how to install such a security solution on your website, read on…
What is an SSL Certificate?
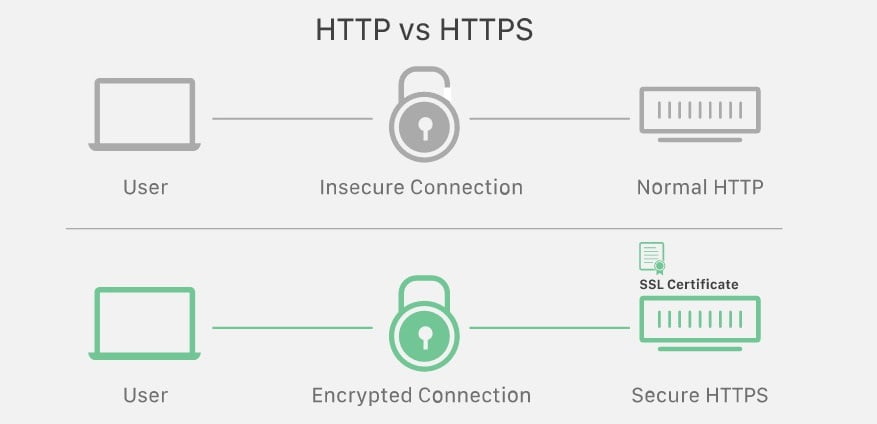
SSL certificates are digital certificates that help websites increase security. This is done in two main ways – proof of identity and encryption.
Applications for SSL certificates need to be verified by organizations called Certificate Authorities (CAs). Depending on the type of SSL, the CA will carry out various verification checks to see if the registrant information is accurate.
SSL certificates utilize private and public keys that help encrypt communications between websites and their visitors. This added security level ensures that anyone who intercepts the data won’t be able to use it.
There are three categories of SSL certificates, namely:
- Domain Validated (DV)
- Organization Validated (OV)
- Extended Validation (EV)
Within these categories, SSL certificates also differ in the number and type of domains they cover. For instance, a single domain SSL is for one primary domain name only. It will not cover any associated subdomains.
SSL Certificate Benefits
Digital security has become an increasing concern over the years. We are living in times when an increasing number of data breaches lead to leaked personal and financial information. One example of this was the Forex trading site FBS that lost over 16 billion data records earlier this year.
As incidents like this are piling up, website visitors inevitably grow more concerned about giving out any kind of information.
Still, SSL certification is helping websites restore some confidence in the security of their data.
It can also:
Increase Visitor Trust
Web browsers today want visitors to be aware of how safe websites are for them to visit. Because of that, visitors can see at a glance if the pages they land on are SSL-equipped. If the website is secure, they will see a padlock icon containing important owner information.
Safeguard Data Transmission
Many websites today require customers to leave some data – and for many reasons too. For example, ecommerce sites need it to process payments and ship orders, while other pages may need information for subscriptions. SSL helps keep data sent between websites and visitors encrypted and safe from unauthorized breaches.
Improve Search Ranking
Google is one of the largest search engines in the world and responsible for most of the organic traffic coming your way. To ensure visitors go to safe sites only, the company prefers to send them towards SSL-equipped websites by default. Not having an SSL can negatively affect your search ranking, resulting in fewer visitors getting to your content.
Mitigate Phishing Attacks
Cybercriminals use a plethora of tactics to steal information, and phishing is one of the most popular ones. However, as more sites get equipped with SSL, it has become more challenging for them to create spoofed sites. Visitors can easily verify the website identity at the click of a button.
Contribute to Regulatory Compliance
Ecommerce sites need to adhere to stricter regulatory standards in terms of security. One of the requirements for PCI compliance is the need to have SSL on the site. Websites must be PCI-compliant to store valuable billing information provided by their clients.
Free and Commercial SSL Certificates
SSL certificates may be essential to security, but they naturally come at a price. But don’t you worry – although there are a fair number of commercial options, free SSL certificates exist and are easily obtainable.
To help make the web a safer place, organizations like Let’s Encrypt offer free SSL solutions. Anyone who owns a website can apply for and use a free SSL, typically DV-type certificates. While not the best, they offer visitors a basic level of site verification.
It is also possible to get free SSL coverage through other service providers. For example, using Cloudflare as a Content Delivery Network (CDN) allows you to utilize their blanket SSL service.
The price for commercial SSL certificates can vary widely – anywhere between $7 to well over $1,000 per year. Prices typically reflect the depth of verification that website owners need to go through. More expensive certificates often come with warranties against loss – sometimes into the millions of dollars.
How to Install an SSL Certificate?
The beauty of SSL certificates is there are several ways you can install them. The methods available to you will also depend on your web hosting package and provider.
Let’s look at two methods you can use. The simplest way is with the help of a web hosting control panel. This graphic-user interface simplifies much of the process, enabling even those new to SSL a smooth and straightforward installation process.
Using AutoSSL for SSL Installation
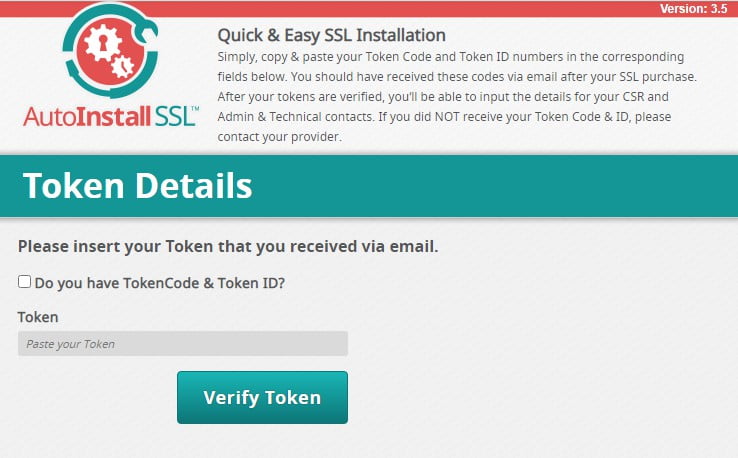
Various web hosting service providers may offer different certificate configuration tools, but the end goal is the same – to ease the SSL installation process. One example of a tool sometimes available on cPanel is AutoSSL.
As the name implies, using AutoSSL is as simple as having your SSL token information in hand. Type whatever information AutoSSL requests in the setup wizard and let the CA do the rest. Of course, AutoSSL isn’t unique, and other web hosting control panel-based tools are available as well.
If you’re using a self-hosted server solution without a control panel, however, you might have to install everything manually. As an example, here is how to do so on an Apache server.
How to Install OpenSSL on Apache Server
Step 1 – Move Your SSL Certificate Files to the Server
When applying for an SSL certificate, you will receive a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). This generates your digital certificate and your public and private keys. You must ensure that you copy these files to the same directory on your web server as instructed.
To make things even more secure, change the file permissions once you’ve uploaded all files. Ensure they are readable only by the root admin.
Step 2 – Locate the Apache Config File
Your configuration file may be located in different folders depending on how you’ve set up your Apache installation. The server’s primary configuration file is usually called “httpd.conf” or “apache2.conf.” and is most likely found in the “/etc/httpd” or “/etc/apache2” directories.
Step 3 – Configure the File and Enter Commands
Once you’ve found your configuration file, create a backup before you edit anything. You can do so with the following command:
cp default-ssl.conf default-ssl.conf_backup
Once the backup is completed, you can edit the config file. The section you have to focus on is Virtual Host. Each type of connection your website can accept needs its own virtual host.
For example, websites that want to operate via secure and non-secure connections must have two Virtual Host sections.
In this section, ensure the following fields are correct:
- SSLEngine on
- SSLCertificateFile – This field contains your certificate location.
- SSLCertificateKeyFile – This field contains your private key location.
- SSLCertificateChainFile – This field contains your CA-Bundle file location.
Step 4 – Run a Command Test
Once you have saved the configuration file changes, run a test to ensure that the changes made are correct. You can use the following command:
apachectl configtest
Step 5 – Restart Apache
Once you verify that everything is fine up to this point, you must restart Apache:
apachectl stop
apachectl start
That is all there is to it. As you can see, even if you have to go through the process of SSL installation manually, the steps are comprehensive and straightforward.
Still, knowing you can rely on your hosting provider for help always brings much-needed peace of mind.
ScalaHosting SSL Solutions
ScalaHosting offers various SSL solutions, ranging from free to paid options. We support the no-cost Let’s Encrypt SSL solutions here, or you can always opt-in for a commercial SSL from GeoTrust and Symantec.
Setting up a certificate with Scala is quite easy as well.
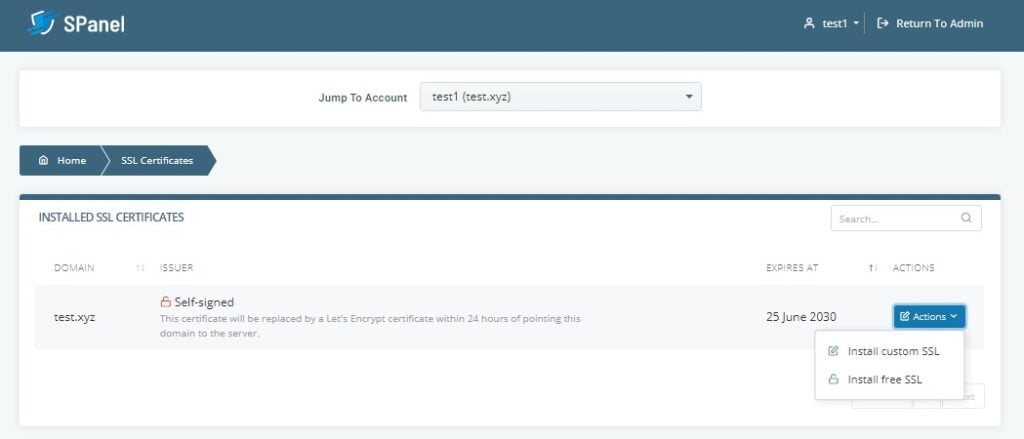
SPanel, our powerful web hosting management panel, is free to use and offers an intuitive SSL installation utility.
To access it, search for SSL certificates on your quick navigation bar. Once inside the tool, you can install either a free SSL from Let’s Encrypt or a custom SSL of your choosing.
Option 1: Free SSL Installation
For free Let’s Encrypt SSL, all you have to do is select Install free SSL. The entire process is automated, and you just have to await the installation confirmation.
Option 2: Custom SSL Installation
If you want to install your own SSL from a third-party provider, simply select the Install custom SSL option. You will need to input some information from your SSL provider – certificate, private key, and CA bundle. The process is automated from this point.

Conclusion
As you can see, there are many ways you can obtain, install, and use an SSL certificate. In fact, with free options readily available, there is no reason why a website today should shy away from secure encryption. Running an online project without an SSL is hindering your progress unnecessarily, especially if you are looking to monetize it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do I know if a web page is SSL-secure?
A: Web browsers will indicate SSL certification with an icon located on the left of your address bar. This icon typically takes the form of a padlock – a locked one showing SSL presence on the site. When you click on it – you should get all verified registrar information.
Q: Why do I need an SSL certificate?
A: SSL certificates serve as proof of domain ownership and encrypt communications between your site and its visitors. If you are running an ecommerce site, SSL certification is also an essential prerequisite for PCI compliance. In terms of search engines – Google has confirmed HTTPS-protected websites rank higher in search results.
Q: What is a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)?
A: CSR is one of the stages to obtain your SSL certificate. It contains information that certificate authorities use to generate your SSL certificate and the public key to be used within. Some of the information included are your domain name, organization, and location.
What is a VPS – Everything you need to know!


