What Is an Email Server?
Emails are the backbone of today’s business world. No matter the size or the industry of the business, the bulk of corporate communication is done via mail, both inside the company and with outside partners and institutions.
And as a lot of sensitive personal and professional information is shared, individuals and firms seek safer and more efficient solutions regarding sending, receiving, and storing e-messages.This is where email servers come into play. In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about them, from what they are and how they work to choosing the right electronic mail host for you and your business.
The Basics of Email Servers
An email server is a computer system that is dedicated to receiving and sending mail. It works with other related programs and applications to create a comprehensive messaging environment that works without any interruptions.
For example, when you send an online message via a program like Microsoft Outlook or Gmail, it forwards the message to an email server. Then, the host scans the transmission and sends it to another location or to a holding space on the same one, depending if the recipient uses the same program as you or a different one.
Benefits of Email Servers
Email hosts offer you quite a few benefits.
First, they allow you to have inboxes with your own domain name, which gives you better credibility and improves brand reputation. If you go for a VPS solution, you can also enjoy enhanced security, thanks to great extras like a dedicated IP or advanced spam procession.
More so, you can easily organize collaborative schedules, as many services offer you shared calendars. Not to mention tailored email functionality like webmail, forwarders, autoresponders, and more. All this enhances your functionality and productivity, making web hosts the perfect choice for your business.
Difference Between Mail Clients and Mail Servers
Mail clients and mail servers are part of the sending and receiving message process. However, they have different roles. A mail client refers to an app that enables you to manage, format, and send online messages.
In comparison, email hosts are software programs that use mail protocols so they can improve the transmission of messages between clients.
More precisely, when you compose a mail and address it to the intended recipient, the host accepts the message, transfers it, and delivers it to the corresponding inbox.
Understanding Email Servers
In order for a computer system to serve as a mail server, it must be equipped with such server software, which allows the administrator to create and manage accounts for the domains.
Additionally, there are two types of e-message servers, including the following:
Incoming Email Servers
Incoming email servers store messages and send them to a user’s inbox. There are two main types, including:
- POP3 or Post Office Protocol 3: They download and store incoming messages on a single device. Then, once the user opens it and downloads the electronic mail, they are automatically deleted from the server. However, you can also keep them. Additionally, most users prefer the POP3 protocol because it is simple, allows you to download and read your mail offline, and is more efficient.
- IMAP or Internet Message Access Protocol: These servers enable you to preview, organize, and delete emails before they transfer them to multiple devices. IMAP hosts also keep copies of them until deleted.
Outgoing Email Servers
Outgoing email servers use the SMTP or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol to manage the delivery process and send e-messages. More specifically, SMTP works with other mail hosts, like POP3 and IMAP, resulting in a seamless delivery and sending process.
How Does an Email Server Work?
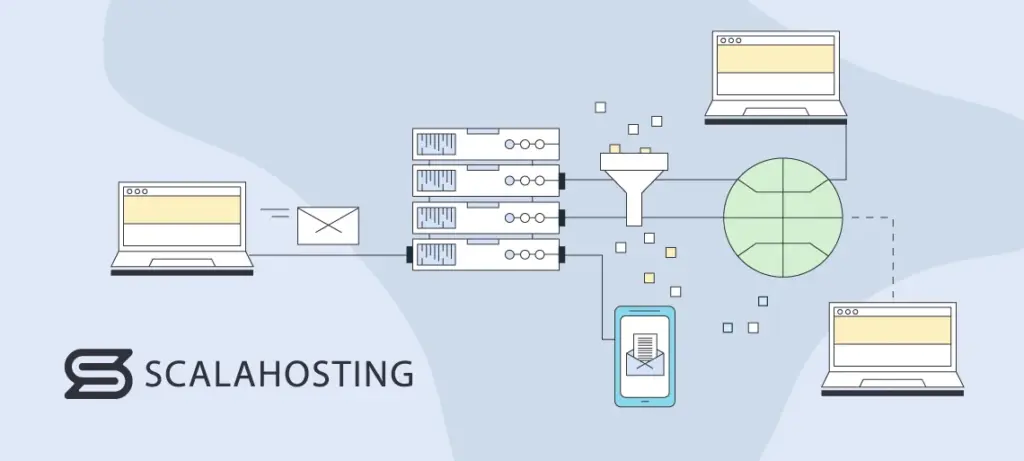
To better illustrate the role of email servers, let’s see what the sending process looks like and what they do to make it happen. It goes as follows:
- The user writes a message and uses a third-party email client to send it.
- The client establishes a connection to the SMTP.
- The SMTP processes the composition and attachments of the mail and identifies the recipient’s address.
- If the recipient and sender have the same domain name, the message is directly transmitted via POP3 or IMAP. Otherwise, if they have different domain names, the SMTP uses the domain name system or DNS, which translates the mail domain name into an IP (Internet Protocol) address, to find the recipient’s server.
- The IP address of the recipient connects to the SMTP host, and once it is identified, the intended message travels through unrelated SMTPs until it reaches its final destination.
- The recipient’s SMTP then handles, checks, and directs the online message over to an IMAP or POP3 server so that it ends up in their inbox.
Email Vs. Web Hosting?
| Web Hosting | Email Hosting | |
|---|---|---|
| Content type stored | Website files and content | Online messages and data |
| Basic features | Website storage space and bandwidth | Mail accounts and server software |
| Plans and pricing | (Typically) A range of plans with different storage and bandwidth limits, as well as features | (Typically) A range of plans with different storage and account number limits |
| Management | Managed by the web hosting provider | Managed by the user or the provider, depending on the level of service and control desired |
| Importance | Important for the performance, reliability, and security of a website | Important for the safety and accessibility of electronic mail accounts and messages |
With email server hosting, you rent a server from a hosting provider for a monthly fee. This solution enables you to cut down on your costs because you won’t have to manage and maintain your own servers.
Also, most providers offer business email hosting, where your own domain is included in your electronic mail address. This can make you appear more trustworthy to customers and partners.
Moreover, the provider you pick can either host your mail on the same server as your website or it can provide a separate one. Of course, you can also choose to host them with different providers if you wish.
Compared to email hosting, web hosting involves the server space for website owners to store their files and data. This allows your customers to access your site and view it online.
In a web hosting plan, you get various tools and technologies within the server space. More precisely, there are software and hardware tools. For example, software tools are a content management system, a web server, and a database, while hardware tools include a network and a storage device.
Quick Summary: What to Look For in an Email Server?
| Supported Emails: | Accommodation for all types of communication services, like webmail. |
| Security Features: | Built-in protection against spam and unauthorized access, encryption capabilities, antimalware, data loss prevention, etc. |
| Mobile-Friendliness: | The ability to send and receive mail on mobile devices when the server is in use. |
| Sharing Options: | Syncing capabilities with web and mobile applications like calendars, distribution and contact lists, and other similar apps. |
| Archiving Tools: | Options for storing and searching for data, regardless of how old it is. |
| Domains: | Ability to include multiple domains. |
The Scala Hosting business e-message hosting service comes with a professional address, advanced SPAM protection, which accurately filters 99.98% of all online messages, and automatic backups, ensuring that you can access and recover your mail at all times.

Conclusion
Email servers are specifically designed to offer a more secure and optimized environment in which online communication is faster, encrypted, and uninterrupted.
To choose the right electronic mail host for your business, you need to look for one that will offer support for all communication services, advanced security tools, archiving capabilities, and other features that will satisfy your needs.
However, if you don’t want to manage and maintain a mail host on your own, you can check out ScalaHosting business email hosting and get an excellent solution for your professional business email.
FAQ
Q: What are the benefits of email servers?
A: Email servers offer many benefits, including:
- It allows every employee or user to have their own email account
- Email servers are secured and don’t allow unauthorized users to access them
- Only users who have the proper credentials can send and receive emails on an email server
- Spam protection is implemented
- Users can set up shared calendars, improving their organization and time management
- It offers excellent privacy and will protect sensitive information much better than regular emails
- It allows you to add as many tools as you want
- You can install anti-virus programs and protect yourself further
Q: What are the limitations of email servers?
A: Some of the limitations that you might face by using email servers include the following:
- Email servers require technical knowledge and skills to run properly
- They need to be maintained daily
- Updates need to be made as soon as they’re available
- They may be expensive for smaller businesses
Q: Email servers vs. emails – what’s the difference?
A: The core difference between mail servers and e-messages is that the servers are physical machines, a.k.a. computers, that have their own system with different services and apps on them. On them, you can store data. Also, you can use them to handle all your e-message traffic, along with domains and everything else that goes into a company mail.
On the other hand, electronic mail is the communication that happens between two addresses. It encompasses complex protocols and processes that are necessary for them to go from the sender to the receiver and vice versa.
Q: Mail vs. Web hosting – what’s the difference?
A: Web hosting includes:
- Website files and content
- Website storage space and bandwidth
- Different plans with various storage and bandwidth limits and features
- Managed by the hosting provider
- Better website performance, reliability, and security
On the other hand, electronic mail hosting refers to:
- Online messages and data
- Mail accounts and server software
- More plans with different storage and account number limits
- Managed either by you or the provider
- Safe and accessible electronic mail accounts and messages
Q: How to secure your email server?
A: There are many ways to secure mail hosts. Namely, you can use many different tools and programs to do so, including the following:
- Installing an SSL certificate
- Getting a S/MIME certificate
- Using DMARC to verify the authenticity of your emails
- Installing firewalls
- Making constant software updates
- Using strong passwords, changing them regularly, and enabling multi-factor authentication
- Using a DNSBL (Domain Name System Blacklist)