What is the Difference Between CDN and Web Hosting?
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and web hosting both serve different purposes. While they make use of many similar technologies, they work best when complimenting each other. Web hosting serves as the core delivery tool of a website, while a CDN helps in other ways.
In the modern era of computing, speed has become a highly defining factor that most websites aspire to. However, web hosting plans typically only allow users to base their websites at one physical location at a time.
Because of latency caused by distance, this could increase the time taken for a web page to load, depending on where information is requested from.
What is CDN Hosting?
CDNs are a collection of interconnected servers dispersed across wide geographical areas. Their purpose is to bring data or applications they are hosting closer to delivery points. Using this method, latency is reduced and delivery speeds are potentially much faster.
Aside from increased delivery speeds, having data or applications mirrored on multiple servers also increases reliability. If one server fails, another at the next closest location can immediately take over until the situation is resolved. Instead of down time, users only need to face slight drops in performance.
There are two general categories of CDN – public and private. Private CDNs require significant capital investment and technical competency to implement. These are mostly used in a business context where the data involved requires additional security.
Public CDNs offer similar benefits and come with much reduced price tags. This is because the cost of using the CDN is shared among a much larger user base.
Differences Between CDNs and Web Hosting
As mentioned earlier, web hosting and CDNs work best when used to complement each other. Let’s examine the ways in which they differ:
Web hosting typically only allows each user the choice of a single server location. Compared to that, CDNs use a network of servers in various locations.
Since data delivery is made in closer proximity, a CDN essentially helps a website to speed up a website by reducing time needed to transport data across longer distances.
Where web hosts serve all kinds of data, a CDN typically only hosts and serves static data. This helps reduce the load on CDN servers so they can be used more effectively in their primary purpose – edge delivery.
CDN Performance
To illustrate the significance of the performance advantages a CDN offers, let’s take a case study and break it down across a few segments. The example in question will consider the traditional web hosting model where the user chooses a Dallas-based server.
As an assumption, we will consider a small CDN with servers located in New York, Germany, and Singapore. If a request was made from Singapore, data would first be served via the server in that country. This helps reduce initial response time to virtually zero.
If we were to have gone with only pure web hosting delivery, there is a big difference. The web hosting server will have to deliver the entire load of data. Since the web hosting server is located in Dallas, data also needs to travel over 15,000 kilometers each way to reach Singapore.
CDN Bandwidth
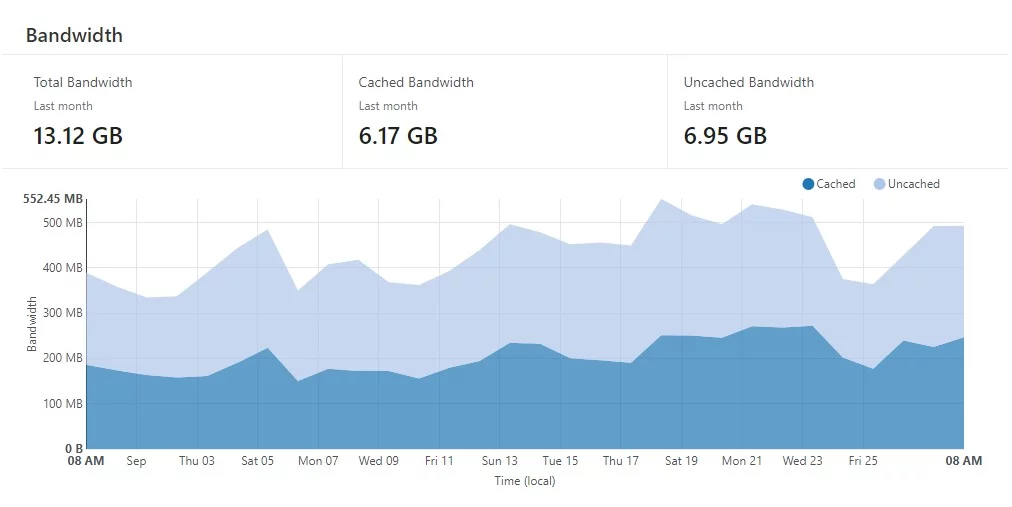
Aside from speed, this delivery of content by the CDN also reduced the load on the web hosting server. The latter only has to deliver the portion of the request which has not been cached on the CDN.
To give an example of this, one website was found to deliver a total of 13.12GB of data using a CDN. Compared to that, the same site was found to deliver 8.52GB of data through its web host across the same period.
This means that the CDN helped reduce the actual server load on the web server by approximately 42%. The amount of data that the CDN can help save highly depends on the nature of the website.
CDNs generally only cache and serve static data. As such, dynamic websites which rely heavily on web applications and databases to retrieve and deliver information may gain fewer benefits.
Hosting Bandwidth
The scenario shared above is brought into even keener focus when taking into consideration websites which use Virtual Private Server (VPS) or better plans. On those plans, bandwidth is typically more restricted.
For example, a typical VPS plan may offer anything between 500GB to 4TB of bandwidth per month. If websites were to deliver large amounts of static data such as multimedia files, the use of a CDN will prove exceptionally beneficial.
Although the general trend has been downwards in terms of cost-per-gigabyte, websites have in general grown increasingly bulky. The rising use of multimedia content such as video and high resolution images has put increased demand on web hosting servers.
This has resulted in overall increases, rather than decreases in cost and bandwidth use rises with the times.
With or Without CDN
In almost all cases, use of a CDN will offer more benefits than drawbacks for website owners. Most of the benefits are very useful both at the individual as well as corporate levels. Further, basic use of a CDN can be cost-free since some do offer some form of free plan to individual users.
Advantages of CDNs include:
- Better speeds due to reduced data travel distance
- Potentially higher load handling capacities
- Improved reliability due to existence of multiple networked server locations
- Better resistance to DDoS attacks
- Savings on cost of bandwidth on web hosting
You also need to take into consideration that these are generic benefits offered by all CDNs. Each brand of CDN also may come with its unique benefits, such as Firewall customization, bot management, SSL protection, and more.
CDN Usage
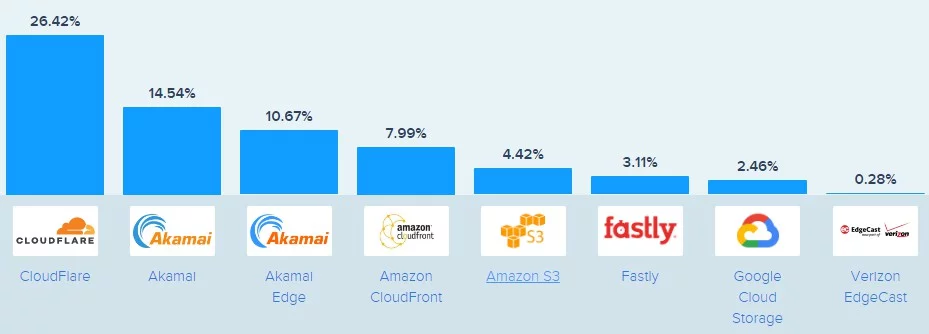
Over the past few years, increasingly large numbers of websites have been adopting the use of CDNs. This can be observed by massively increasing amounts of data being served through CDNs.
In 2017, CDNs delivered 54 exabytes of data. That figure doubled in two years and is expected to double again to reach 190 exabytes by 2021. Among the various CDN providers, Cloudflare has remained the dominant brand. Its servers help facilitate the flow of more than a quarter of all CDN-served data from over two million websites.
There have been some claims that CDNs have been making traditional web hosting plans redundant. However, as you can see, this isn’t really the case since they act in a complimentary manner.
Web hosting for now, remains as the core product, with the use of CDNs helping by increasing performance.
Web Server Usage
In most scenarios, web hosting plans offer users a few core resources that they need to be observant of. These include CPU utilization, memory, storage space, and resources. Among that list, storage space is typically (not always) the lesser concern.
CPU utilization and memory together combine to affect the levels of strain on a web hosting server’s load. If the web host is being asked to serve more requests than its limits allow, the website in question may start to exhibit abnormal behavior patterns.
These can include:
- Higher than usual load times
- Occasional page load failures
- The site completely crashing
Using a CDN can help to reduce the potential load on a web hosting server’s resources. Since the web hosting server itself needs to deliver less data, the CDN effectively allows it to exceed its typical load capacity.
Conclusion
The ‘extra’ capacity that using a CDN offers should not be taken as free reign to stress your web server to its limits. Instead, take advantage of the extra allowance to better cope with temporary traffic spikes.
Always ensure that the resources you’re really using stay below the limits of your web server – not taking into account the CDN. This way you can avoid potential issues with the site from cropping up.

Frequently Asked Questions
Is CDN a web server?
CDNs are networks of servers designed to distribute data delivery over large areas. They are not replacements for web hosting servers, but act in a similar capacity in some ways.
Should I use a CDN?
Yes, use of a CDN is advisable. In almost all scenarios, using a CDN as an additional resource to support your web hosting server is a good plan. They help increase performance, reduce bandwidth consumption, and help with server load as well.
Why is CDN faster?
CDNs work by caching static content at various locations around the globe. When a request is made, the CDN will respond first by serving the data it has from the location closest to where the request was made. This helps reduce response time by limiting latency.
What is the purpose of CDN?
CDNs are designed to extend the edge of web hosting delivery points. Instead of only delivering data from one point, the network of servers will be able to serve data from multiple locations.This helps reduce time taken for initial response to any request.
Is CDN secure?
Although CDN servers are generally secure, using them to transmit sensitive data can be risky. For situations where data security is vital it is advisable to consider the use of private rather than public CDN servers.