The web hosting industry comprises many services, components, and underlying technology. Seeing as each site needs hosting to exist on the Internet, it is vital for owners to know what goes into website hosting so they can understand what their business needs.
However, this can often be overwhelming, especially for newcomers that have yet to gain prior experience or specialized knowledge. Hosting encompasses so many things that it’s natural for some users to need clarification.
So, to make this service easier to grasp, we will discuss the differences between server, host, virtual host, and VPS, see what each is, and what it is used for.
Let’s begin!
Explaining What a Server, Host, Virtual Host, and VPS Are
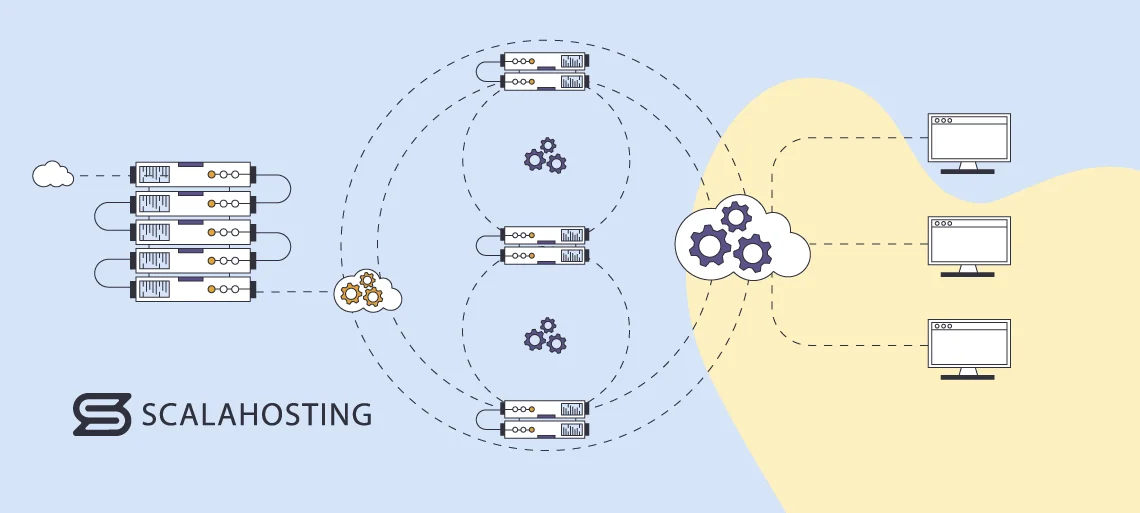
To truly understand the difference between server, host, virtual host, and VPS, we first must learn what each one is.
What Is a Server?
A server is a piece of computer hardware or software that provides services to another computer program/device and its user/client. In the client-server programming model, the server program performs tasks and requests from the client program.
There are many types of server solutions, each with at least two software components, including an operating system and an application.
What Is a Host?
A host is any computer system connected to a network that provides all types of data, features, resources, and other services to clients and devices within the same network.
Users can access the host network via different means, including a user interface, specialized software, and a network address.
Any kind of device can be used to host data, including servers, centralized mainframes, personal computers, and multi-functional devices.
What Is a Virtual Host?
A virtual host refers to a single server that can power and deploy multiple websites on one machine. Namely, virtual hosts provide online infrastructure solutions to numerous users simultaneously, including servers, computers, and storage via the Internet.
Such solutions enable clients to access their data and services remotely from any device. Additionally, you can isolate users on the same server with virtualization software, allowing you to supply each of them with their own resources, like CPU, RAM, and bandwidth.
What Is VPS?
A virtual private server, or VPS, is a virtual machine that delivers all the resources and applications a website needs to operate smoothly online. Similarly to virtual hosts, VPS solutions utilize virtualization technology to split a physical server into multiple virtual instances, enabling the provider to host and deploy multiple sites from one machine.
The private aspect of VPS means that each user gets their own set of system resources and is not affected by the performance of the other websites they share the physical server with.
Use Cases and Applications of a Server, Host, Virtual Host, and VPS
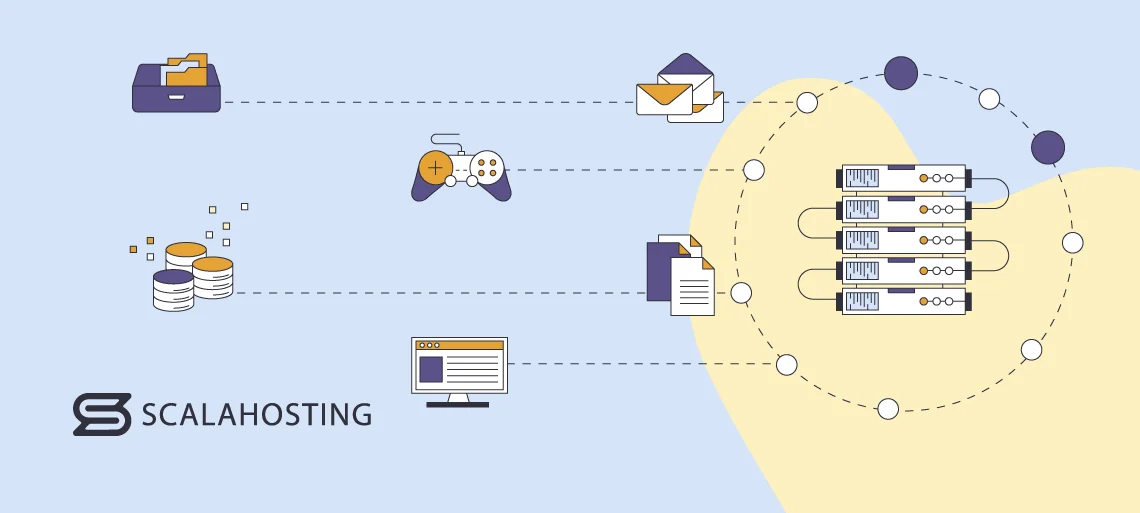
Now that we know more about servers, hosts, virtual hosts, and VPS solutions, let’s learn more about their practical application.
Server Use Cases
Servers are highly flexible and powerful computers that can provide numerous services and functionalities depending on the client’s needs.
Some of the most common use cases of servers include the following:
- File server: Servers can be used to store and manage client data and enable them to access and share files over a network. This gives users a centralized destination where all their data is located, making daily operations more fast and efficient.
- Web server: These servers host websites and deliver web pages to end users that want to access them. They do this by processing HTTP requests and serving web content to browsers, like HTML, images, and multimedia files.
- Application server: Clients can use application servers to host and execute apps or software services. This server performs tasks like transaction processing, database management, and application deployment.
- Database server: A server that manages and provides access to databases. It also stores, organizes, retrieves, and updates data, providing users with a more efficient way to perform database operations.
- Email server: These types of servers utilize various protocols, including SMTP, POP3, and IMAP, to enable more efficient email communication. Moreover, email servers handle the sending, receiving, storing, and retrieving of messages, ensuring that the client never misses an important message.
- DNS server: Domain Name System (DNS) servers convert domain names into IP addresses, which allows users to access websites using their domain names. Additionally, they help resolve domain name queries and manage domain records.
- Backup server: These servers perform data backups and recovery by automatically storing copies of information from the client’s devices or other servers. This, in turn, ensures that the user does not lose their data and can quickly recover it.
- Virtualization server: With this server, users can create and manage virtual machines and host multiple operating systems and apps on one physical server.
Host Use Cases
Since hosts supply all types of data and resources to their clients, they can be used to provide many different services, including:
- Web hosting: One of the core host functionalities is providing traditional web hosting services, which enables you to deploy your website and make it available to customers online.
- Cloud hosting: This is a hosting type that uses cloud technology to deploy resources and data to end users via the Internet. Additionally, cloud hosting involves using a network of physical and virtual cloud servers to host multiple websites with enhanced scalability, flexibility, and reliability.
- Remote hosting: Remote hosts employ servers located in data centers to store and deploy files and resources to clients. To access their data and apps, users log into the server via an internet connection.
- Mainframe computer environments: Hosts can be used to provide mainframe computers with massive computing power and storage capabilities to clients that work with large data loads and need an extensive network to conduct their operations.
Virtual Host Use Cases
Some of the most common use cases of virtual hosts include:
- Shared hosting: Because virtual hosts deploy multiple websites or apps on a single server, they are often used in shared hosting environments to provide each user with their own website, email account, and other resources.
- Development and testing: Developers use virtual hosts to create multiple environments where they can develop, test, and stage their projects and apps.
- Ecommerce platforms: Online shopping platforms use virtual hosts to provide individual stores for each user. Each shop they deploy can operate under its own domain name and utilize dedicated resources not shared with any other stores on the platform.
- Content management systems: CMS platforms like WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla use virtual hosts to manage and host multiple sites from a single server. This way, each website gets separate administration, design, and content.
- Multilingual sites: With virtual hosts, website owners can create and deploy multilingual sites with different domain names and provide localized content and user experience based on the language their target audience speaks.
VPS Use Cases
VPS provides excellent flexibility and resource scalability, ideal for many different purposes, including:
- Web Hosting: The most common use of a VPS is for hosting multiple websites from a single physical server and providing each user with separate resources that they can further customize.
- Remote desktop access: With virtual private servers, clients can access their desktops and workstations from anywhere, which is perfect for companies that operate entirely online.
- Gaming servers: Virtual private servers are excellent for hosting game servers for multiplayer online games because they provide all the resources needed for smooth gameplay. They also allow gamers to customize their settings, mods, and in-game configurations.
- Proxy and VPN servers: Because VPS solutions provide a secure and private connection for accessing online content, they work great for setting up a proxy server or a Virtual Private Network (VPN).
- Data storage and backup: A VPS can be used as a remote backup location or file storage solution, enabling users to keep their important documents and data in a secure and easily accessible place.
- Data analysis and processing: Clients can use a VPS to deploy their data-intensive tasks like extensive data analysis, machine learning, or problem simulations.
- Hosting online services: VPS plans are an excellent solution for hosting email servers, FTP servers, CMSs, and ecommerce platforms.
The Key Differences Between a Server, Host, Virtual Host, and VPS
| Server | A physical or virtual computer or hardware device that supplies other devices within the same network with resources and services. |
| Host | A service provider that uses a computer system to provide clients with server resources and infrastructure. |
| Virtual Host | A single server that hosts multiple websites and services. |
| VPS | A virtual machine that imitates a dedicated server within a shared hosting environment, enabling users to get their own resources at a lower cost. |
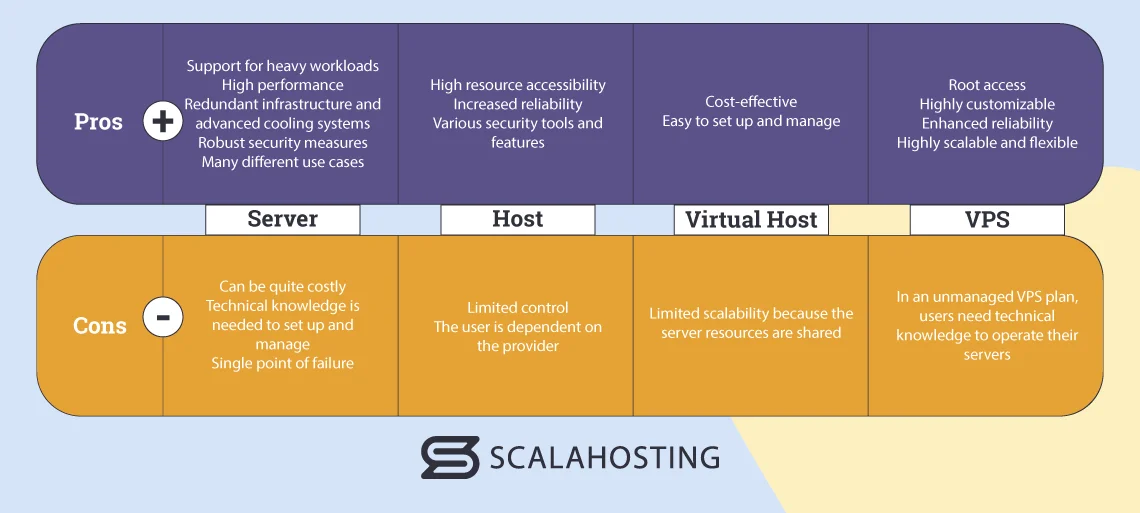
Server, Host, Virtual Host, and VPS Pros and Cons
| Server | Host | Virtual Host | VPS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pros | Support for heavy workloads High performance Redundant infrastructure and advanced cooling systems Robust security measures Many different use cases | High resource accessibility Increased reliability Various security tools and features | Cost-effective Easy to set up and manage | Root access Highly customizable Enhanced reliability Highly scalable and flexible |
| Cons | Can be quite costly Technical knowledge is needed to set up and manage Single point of failure | Limited control The user is dependent on the provider | Limited scalability because the server resources are shared | In an unmanaged VPS plan, users need technical knowledge to operate their servers |
The ScalaHosting managed VPS service helps you deploy websites on the ultra-fast LiteSpeed web servers that provide fast loading speeds and excellent performance. Additionally, all plans are equipped with a wide variety of features and packed with enough CPU, RAM, and disk space even for high-demanding projects.
Conclusion
Servers, hosts, virtual hosts, and VPS solutions serve different purposes in the web hosting world. When choosing your hosting provider, check out what kind of servers it uses for hosting sites. Additionally, if you want to host your website on a VPS, ensure you get a host that offers a highly-optimized environment that will supply you with everything you need.
Check out our excellent managed VPS hosting plans that come with top-tier management and development tools to give your online project a much-needed boost.

FAQ
Q: What are the most common types of servers?
A: Even though there are many types of servers, some of the most common ones include the following:
- Web server
- Database server
- Web proxy server
- Email server
- FTP server
- DNS server
- DHCP server
- File server
- Gaming server
Q: What is the primary difference between a physical server vs. virtual server?
A: A physical server is a piece of hardware that can be found in data centers. On the other hand, a virtual server is an isolated instance on the physical machine. A process called virtualization allows hosts to split any physical server into multiple virtual ones and allocate a set amount of system resources.
Q: What can you do with a virtual host?
A: A virtual host is a service that enables more than one website to exist on a single web server or system. Every website hosted on a virtual host is differentiated by its hostname or IP address. This solution allows multiple companies and individuals to host websites on the same server while keeping their own domain names and IP addresses.