The seemingly simple task of finding the right hosting service for your website is often fraught with difficulties, especially for those who haven’t been through the process before.
First, you need to sift through hundreds of providers, all promising tasty discounts, impressive uptime stats, and a smooth experience all the way.
You also have to go through the different types of service. Technically, all plans you will be looking into are designed for website hosting, but their prices and the features they offer vary wildly, and making the distinction between the available options is often quite tricky.
For example, many people struggle to distinguish between regular VPS hosting and cloud hosting.
Today, we’ll try to clear up some of the confusion.
What is a VPS?
Before we get to the differences between VPS hosting and cloud hosting, we should first talk about the technology that enables both services – virtualization.
Thanks to virtualization, you can create a virtual machine (VM) and deploy it on top of your physical hardware. Effectively, you have a computer running inside another computer. Here’s an example:
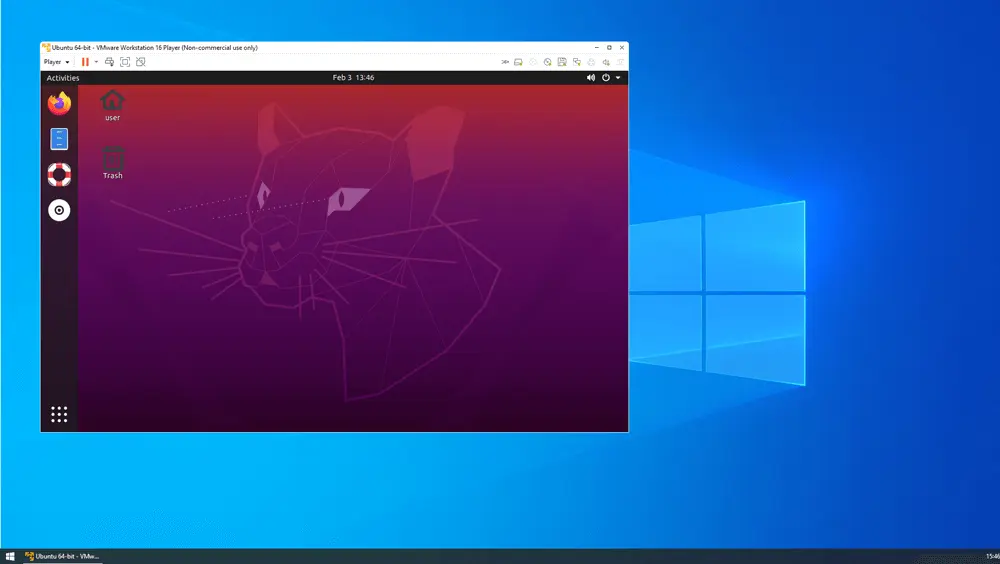
In the screenshot above, you can see an Ubuntu virtual partition running inside a Windows desktop PC. It was set up with VMware Workstation Player, a free application that creates a virtualization layer on top of your home computer’s hardware. The Ubuntu guest uses the host’s resources, but you can run operations on it independently from the Windows environment.
The virtualization solutions hosting providers use are not too dissimilar, though the setup is more sophisticated. Hosts deploy and run multiple virtual machines (in the context of web hosting, they are usually referred to as virtual servers or virtual private servers/VPSs) on the same hardware.
Each VM has its own operating system, a dedicated IP, and a predetermined set of hardware resources reserved for it. The virtual machines are completely independent, and even if one of the VPSs is under heavy load, this won’t affect its neighbors in any way.
Both VPS and cloud hosting accounts give you access to a VM such as the ones described above, and the benefits compared to cheap shared plans, for example, are immeasurable.
The choice of an operating system makes virtual server solutions much more versatile. Thanks to the isolated environment, the performance is more stable, and the dedicated IP gives your VM better security.
All these advantages are available for both VPS and cloud hosting users. The differences lie in the way the VMs are deployed.
Cloud Hosting Overview
The concept of cloud computing revolves around the way websites and applications access the resources they need to run. In the context of web hosting, the resources in question include:
- Storage space
- Memory
- Processing power
When providers take multiple servers and connect them to a common network, they create an enormous pool of resources called a cloud. With virtualization technology, they can efficiently distribute these resources among many virtual machines.
The component responsible for deploying and managing the cloud servers is called a cloud hypervisor. Through it, providers can start and stop individual VPSs and allocate different hardware resources to them.
Several factors make this by far the best hosting setup of them all.
From a provider’s perspective, a cloud VPS service enables efficient utilization of hardware resources, which is critical for their profit margins and ability to provide a high-quality service at a reasonable price.
However, the benefits are even more significant for site owners and developers.

Cloud VPS Hosting Pros and Cons
Cloud VPS hosting is the latest trend in the hosting industry, with some experts predicting that it can all but eliminate the need for all other types of services. This may seem like a bold prediction, but you probably shouldn’t discount it, given the innumerable advantages a cloud-based virtual server gives you.
First, let’s compare it to the cheapest and most common hosting service – shared hosting.
Right off the bat, you get a lot more bang for your buck. With a shared server, the resources of a physical machine are distributed among hundreds of websites all hosted on it. The power you get depends on how many people are on the same server and how much load it’s under.
A cloud VPS is a lot different. Picking a cloud server for your website is a lot like choosing hardware components for your home PC – you get to decide how much processing power, RAM, and storage space you’ll have. These resources are available all the time, no matter what. This means faster, more consistent loading speeds and much more predictable all-round performance.
Your cloud server also has a dedicated IP. You’re the only one using it, so you don’t need to worry about someone else ruining its reputation or putting your project under threat.
All in all, a cloud VPS shares some of the main advantages of a dedicated server. In both cases, you have a completely isolated environment reserved specifically for your website, leading to better security, reliability, and complete independence from other people’s projects. However, there are also some differences that turn the virtual server into a more attractive proposition.
First, you have the flexibility. Most dedicated servers are quite powerful, but they’re also very expensive, and although you have a lot of resources at your disposal, you don’t necessarily use all of them all the time.
A real cloud server has a fully customizable hardware configuration. The number of CPU cores, the RAM, and the storage can be tweaked according to your project’s requirements. You don’t need to settle for a fixed plan that forces you to pay for resources you won’t use.
And if more resources are required, adding them is much easier than it would be with any physical machine.
Upgrading your dedicated server plan could take hours. A new machine has to be set up, your website moved to it, and the domain redirected correctly. Quite a lot could go wrong, and not all hosts are willing to help with the process.
By contrast, upgrading a cloud server takes a couple of clicks. You can usually do it via the client area on your host’s website, and it rarely requires anything more than a quick reboot of the virtual machine.
You can easily scale down as well. This flexibility enables cloud providers to give you a “pay-as-you-go” system that is simply not possible with another hosting setup.
As if that wasn’t enough, a cloud VPS server is also more likely to give you the high availability you’re after.
A hardware problem on the dedicated server hosting your website would be a major emergency. The data center would have to dispatch a technician who would physically go to the machine, diagnose and fix the issue. Best case scenario, there will be another physical machine ready to go, but even if there is, restoring your website on it could take hours.
If you have a cloud VPS, this isn’t a problem. At any given time, your VPS is running on one of the machines in the cloud. If there is a hardware failure on that machine, the hypervisor simply moves the virtual server to another node. The VPS is up and running in minutes, and website owners rarely even notice that something has gone wrong.
Overall, cloud hosting has quite a few advantages over other services on the market. But how does it compare to traditional VPS hosting? And what are the differences, exactly?

Overview of Traditional VPS Hosting
We already established that both cloud and traditional VPS hosting give you access to a virtual machine that hosts your website. The difference lies in the way resources are deployed.
Like a cloud VPS, a regular virtual server has a dedicated IP and predetermined CPU cores, RAM, and storage space available to you anytime. Every VPS has its own operating system and works independently.
The difference is, instead of a cloud of physical servers providing an enormous pool of resources, you have a single machine powering multiple virtual instances.
This may seem like a minor dissimilarity, but it’s actually more significant than you may think.
VPS Pros and Cons
Traditional VPS solutions have the same advantages over shared hosting as the ones deployed in the cloud.
You can choose between different operating systems, allowing you to host an infinite range of projects. The resources are guaranteed and available all the time, so you can expect more consistent loading speeds and solid performance. Depending on the package, you may also get root or administrator access, letting you customize the hosting environment to your specific requirements.
You once again have a solution that resembles a dedicated server without costing an arm and a leg.
Pit a traditional VPS against a cloud-based virtual server, however, and you’ll see that there are downsides, as well.
For one, traditional VPSs can also be scaled up, but they are limited by the capacity of the underlying hardware. The more VPSs you have running on the same physical server, the less room you have for them to grow. And as some users add resources to their virtual machines, there’s less unused hardware left for the rest. Eventually, the physical server will be full, and users will have no ability to scale up. These limitations also make the resource distribution less flexible.
Traditional virtual servers aren’t fully customizable. To utilize their hardware more efficiently, providers of traditional VPS hosting only offer preset plans, so you don’t get to choose the exact configuration yourself.
It’s a far cry from the pay-as-you-go system offered by cloud plans.
Your entire project depends on the physical server staying up, as well. If a piece of hardware on it fails, your VPS, along with the rest of the virtual machines hosted on the same server, will also be knocked offline. Bringing the server back up is a complex task that could take hours.
Because your VPS isn’t in the cloud, you can’t just deploy it on another machine and be up and running in no time.

VPS or Cloud Hosting: What Should You Choose?
Both VPS and cloud hosting have more than a few distinct advantages over traditional shared and dedicated hosting. But how do you choose between them? Let’s do a quick head-to-head.
| VPS Hosting | Cloud Hosting | |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | The virtualization technology allows hosts to easily modify a virtual server’s hardware configuration, so if you need a more powerful solution, you can usually get one. However, because your VPS is ultimately limited by the physical machine’s hardware resources. | Your hosting service is powered by a cluster of powerful hardware machines, which means it can tap into a practically unlimited pool of hardware resources. Some cloud providers can even dynamically adjust the amount of power you have based on your usage. |
| Uptime | While reputable VPS hosting providers can offer you pretty decent uptime stats, a standard VPS hosting service is ultimately dependent on the health of the physical machine powering it. If it goes down, all the virtual servers hosted on it follow it. | The cloud cluster offers high availability and a reliable failover mechanism. Your hosting service is powered by multiple physical machines that work together. If one of them fail, the rest take up the slack immediately, eliminating any noticeable traces of service disruption. |
| Performance | A virtual private server offers a fully isolated hosting environment, meaning that, unlike shared hosting, it comes with guaranteed resources and much more consistent loading speeds. However, the performance ultimately depends on the size of your website and the optimization techniques you’ve implemented. | The flexibility offered by the cloud cluster lets you have the exact resources you need when you need them. Couple this with the fact that a well-built cloud infrastructure gives you pretty much unlimited scalability, and you get blistering loading speeds even for large-scale, complex projects with lots of traffic. |
| Security | Your VPS functions as an individual machine, so its security depends on the tools used for protecting the server and their configuration. If you opt for a managed service, you’ll get them set up and ready to go. On a self-managed server, you’ll have to configure them yourself. | The security setup of your cloud hosting account depends to a large extent on the nature of the service. For example, some providers offer virtual servers based on a cloud infrastructure, in which case the protection mechanisms are the same ones you’d use on a VPS. In other cases, the security of your data is much more dependent on your provider. |
| Pricing | Most VPS hosting services are based on monthly or yearly subscription models, with upfront payments. | Thanks to cloud hosting’s flexibility, providers can offer an extremely convenient pay-as-you-go pricing model, which allows you to pay only for the resources and bandwidth you’ve used. |
How to Choose The Right Cloud Hosting Service For You?
From what we’ve seen so far, we can conclude that cloud-based virtual servers are superior on all fronts compared to regular VPSs and other forms of traditional web hosting. However, our work is not done just yet.
There are several variations of cloud hosting, and choosing the right one is essential if you want the right service quality at the right price.
Which aspects of the available options you’ll look into first depends on whether you’re a single user or a business organization.
Business solutions.
Cloud computing opens a number of opportunities for businesses of all shapes and sizes. However, to take full advantage of it, you must pick the right infrastructure.
- Public cloud.
Services that fall into the “public cloud computing” category are offered by companies like Amazon, DigitalOcean, etc. These providers build enormous clouds spread across dozens of data centers and use them to host their clients’ VPSs.
This means that in a public cloud, you use the same cluster of physical machines as thousands of other clients. This keeps cloud hosting costs down.
- Private cloud.
In a private cloud, you have the cloud cluster to yourself. It’s reserved exclusively for your virtual server(s), with no other people having access to the same machines.
Companies opt to create their own cloud clusters when their projects require extra security. Indeed, the setup is worth considering if your company deals with sensitive data on a daily basis. However, you must remember that setting up a private cloud is quite expensive.
Another thing you have to bear in mind is that the level of security a private cloud provides depends on a number of different factors. Setting it up correctly requires a lot of technical expertise, and you need to ensure you have access to it before you start building your private cloud.
- Hybrid cloud.
As its name suggests, a hybrid cloud setup combines the two deployment methods outlined above. There are a number of ways to set up a hybrid cloud cluster, but in all cases, some of the components are provided by a public cluster, while the rest come courtesy of a private cloud or on-premise hardware. The idea is that you can experience the benefits of two or more deployment methods without any of the drawbacks.
- Managed cloud cluster.
If you have a really busy website or a mission-critical application, a single cloud VPS may not be enough. Traditional alternatives offer little in terms of benefits, so at ScalaHosting, we decided to create a service that takes cloud hosting’s availability and scalability to the next level.
Instead of a single virtual server, you get a cluster of VPSs working together to provide you with blistering performance and impeccable reliability. Our state-of-the-art solutions can even cluster VPSs deployed across multiple physical networks in different locations, so you can guarantee excellent speed in all corners of the globe. A load balancer ensures the load is spread evenly, and if, for some reason, one of your virtual machines becomes inaccessible, the rest of the nodes in the cluster take up the slack immediately, with no downtime or loss of performance whatsoever.
ScalaHosting’s cloud clusters are infinitely customizable and scalable. Our technical experts will review your project before recommending the best solution for it. Then, they’ll build the cloud VPS cluster for you, and since the service is fully-managed, they’ll be on hand to ensure the security and performance are at the required levels.
Meanwhile, you get to manage the projects hosted on your cloud VPS cluster through SPanel – ScalaHosting’s proprietary control panel designed to help you easily develop and run your website in a cloud hosting environment.
Check out our page dedicated to our cloud cluster service, and don’t hesitate to contact our experts, who’ll get you started.
Solutions for individual users.
The information above pertains to large business organizations with many employees and projects that generate lots of traffic and revenue. If you’re an individual user or a web development agency looking for a cloud VPS to host your customers’ websites, you have other things to worry about.
First, you must ensure the hardware resources will be sufficient to give your site(s) the performance you’re after. After you’ve done that, you can move on to another aspect of the service that is equally important.
While looking into the available options, you’ll see that VPSs can be managed or self-managed.
Being able to distinguish between the two is important.
- Self-managed cloud VPS.
A self-managed cloud VPS is more suitable for people with at least some server management experience. Your host deploys the virtual machine and installs an operating system on it. In some cases, you have the option of getting a control panel, as well.
From then on, your host is responsible for keeping the server online, and that’s about it.
It’s up to you to install the applications and utilities you need to run your website and configure all your server’s components so that the VPS runs smoothly and securely. You get root access to set up additional tools your project may need, configure the firewall, etc. Once everything is up and running, you need to keep it that way.
You’ll need to monitor the server’s performance and take the appropriate actions if it’s slowing down. You’ll also need to keep your eyes peeled for any newly-discovered vulnerabilities in the software products you use. Whenever a security hole pops up, vendors hurry to release an update to plug it. With a self-managed server, it’s up to you to install the update, and you can’t expect any help from your host’s support team.
Overall, running a website on a self-managed server is a lot of work. So, why would anyone opt for it?
If you have a self-managed server, you’re free to install whatever you want on it (as long as you’re not breaking your host’s terms of service, of course). You can customize the hosting environment to your exact specifications, so it’s the perfect solution if your website uses technologies that are not supported on a managed plan.
Self-managed VPSs also tend to be cheaper than their managed equivalents, so they may be a good solution if you are an experienced sysadmin who wants to save a few dollars.
If you’re not an experienced sysadmin, however, paying the extra for a managed server is definitely worth it.
- Managed Cloud VPS.
A managed VPS comes ready out of the box. Your host deploys the virtual machine, sets up the operating system, and installs everything you need to build and run your website.
When you get access to the machine, a stack of technologies is already installed, configured, and ready to go. A typical managed VPS also has a mail server taking care of your email communication, a firewall protecting your project, and a host of other utilities optimizing the server’s performance and security. All these are the responsibility of your host’s technical team.
They’ll ensure the components are up and running at all times, apply the proper configuration for optimum performance, and install updates to guarantee that you have access to the latest features and security patches.
Meanwhile, you can focus on building your website, and you have an easy-to-use platform that helps you with it. Let’s take SPanel as an example.
SPanel is a proprietary control panel developed by ScalaHosting and optimized for cloud VPS solutions. It’s available on all our cloud hosting plans (both managed and self-managed), and you can also get a license and use it on your own virtual or physical server.
There are two types of SPanel accounts – Users and Admins.
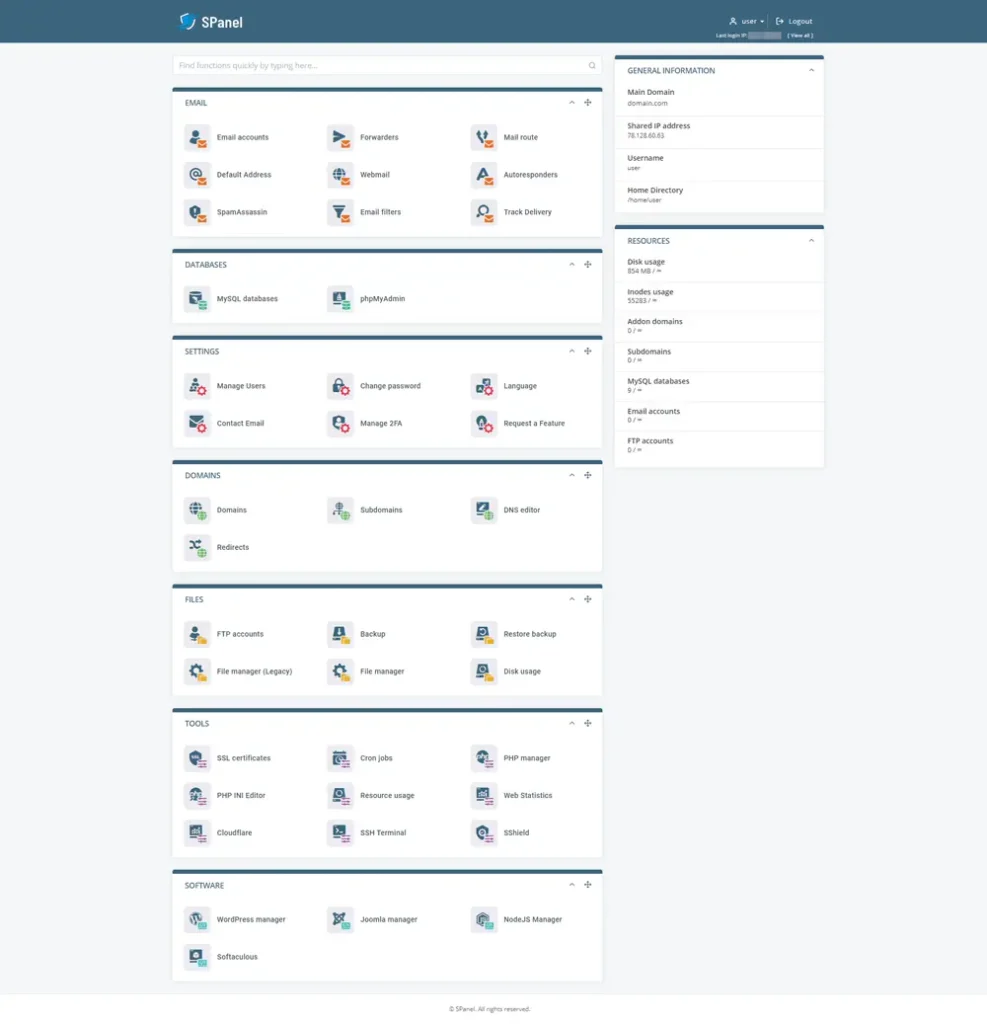
From the User Interface, you can automatically install a CMS application, manage files, databases, and email accounts, set up SSL certificates and DNS records for your domains and subdomains, and many more.
In the Admin Interface, you’ll find yet more tools for controlling and managing your VPS and the components working on it. For example, you can create, suspend, terminate, and set quotas on individual user accounts. Detailed information regarding the server load is available on the homepage, and you can view and restart services and manage API tokens.
If you want more speed for your websites, you can swap the default Apache web server for a setup that works with Nginx, LiteSpeed Web Server, or OpenLiteSpeed.
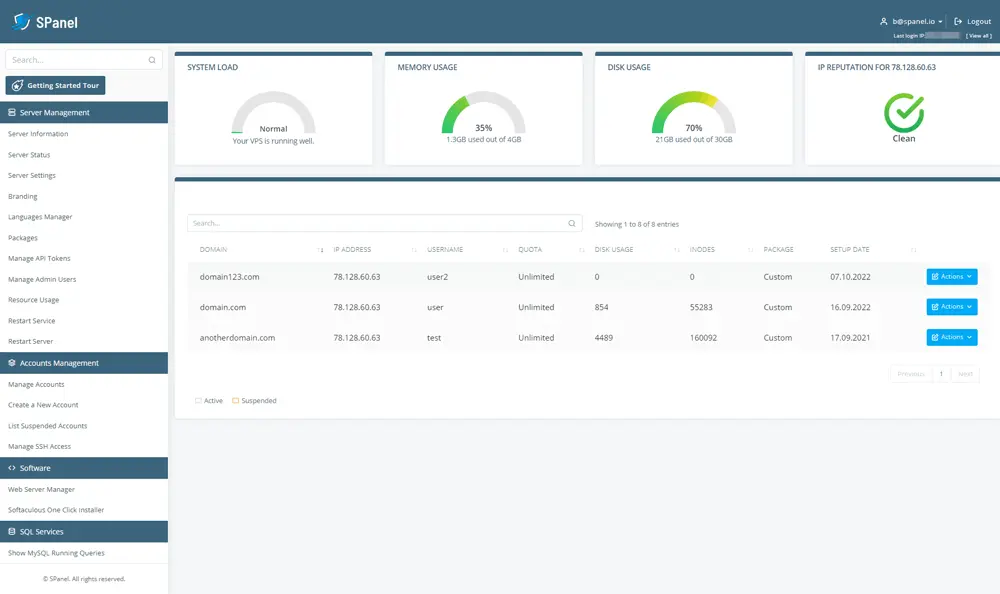
In summary, thanks to SPanel, you can create and manage your websites on your own server without any advanced technical skills. As you can see from the screenshots, the interface is intuitively laid-out, and you can use it without knowing the first thing about commands or system administration.
Conclusion
There’s a lot of confusion around the differences between cloud VPS and regular VPS hosting. Indeed, there are quite a few similarities, but there are also several key differences that make a huge impact on the service’s reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
When you understand what they are, it will be easier to figure out which one’s right for you.
FAQ
Q: Is VPS the same as cloud hosting?
A: No, it’s not. In a traditional VPS setup, your web hosting provider sets up multiple virtual machines on a single server and then rents them out to individual clients. On a cloud hosting plan, you get a virtual server that can tap into a pool of resources provided by a cluster of interconnected physical machines.
Q: Is VPS a cloud service?
A: Virtual Private Servers can be put in a cloud environment. However, in its more traditional implementation, VPS hosting is not a cloud service.
Q: What is the difference between VPS and dedicated hosting?
A: With a dedicated server, you get an entire physical machine to yourself. You usually have root access, and all the machine’s server resources are at your disposal.
To create VPS hosting, providers partition a physical server into several virtual machines and lend them out to customers. You still have a fully isolated environment, but the plan is much more affordable since the hosting company can distribute the physical server’s resources among multiple accounts.
What is a VPS – Everything you need to know!