Visitors will get a No Found error or Error 404 when you move a page to a new location, resulting in loss of traffic and probably sales.
However, savvy web admins often mitigate this with web redirects which take the visitors to the new location without them even knowing.
This article guides you on everything you need to know about web redirects, including when to use them, the type to use in different scenarios, and how to write and implement redirect codes.
So let’s get to it.
What’s Web Redirect?
Web redirects forward traffic to the new location when a page moves or gets deleted.
It lets users take their website visitors to a new page when its content becomes unavailable in its previous location. But if there is no redirect, people visiting a moved or deleted page will see an annoying error, making the user experience seamed.
Suppose you move a page, let’s say, from www.domain.com/photos to www.domain.com/media.
If you set up a redirect to the new URL, when older visitors try to access your web photos using the old URL they are more familiar with, their browsers forward them to the new URL, preventing them from seeing the error page.
Web Redirect Use Cases
Web redirect makes navigation and user experience seamless for visitors and search engine spiders, enabling users to retain older visitors and indexed pages on search engine results.
But too many redirects could slow down your website, so only use it when necessary, which could include:
- If a web page moved to a new URL on the website or another website
- When you move your website to a new domain name and wish to forward traffic to the old domain to the new website
- After parking a domain name—allows you to point different domain names to your main website
- Redirecting HTTP to HTTPS to force all visitors to connect securely to your website
- To redirect non-www URLs to the www version or vice versa to prevent duplicating web content
Types of Web Redirect
You could choose your redirection type depending on the end goal. So, let’s examine the main types of web redirects.
Permanent Redirect
Permanent redirect, also known as 301 redirect, indicates that the page has moved permanently to a new URL, as the name suggests.
It’s helpful if you don’t wish to bring back the old URL.
The redirect returns status code 301 when someone or user-agents (web spiders) visit, requesting the web server to re-route the page to the specified URL.
A 301 redirect passes on the authority that comes from the old page’s backlinks to the new one, making it essential for search engine optimization (SEO).
Temporary Redirect
Temporary redirect or 302 redirect indicates temporary relocation.
It forwards visitors from a page to another temporarily, indicating to browsers and user agents that the URL is on a temporary location.
Here are when to use temporary redirect:
- If you wish to send visitors temporarily to another page while updating a page
- When carrying out website maintenance
- If you want to test a new page and get customer feedback without removing the old page
Writing Web Direct .htaccess Codes
You can create a web redirect by adding some lines of code on your domain’s .htaccess file—a server configuration file that allows users to modify their server settings.
We’ve put together some sample codes to get you started.
Permanent Redirect Codes
You can redirect permanently to another URL on the same website by adding this code to your .htaccess file.
Redirect 301 “/photo” “/media”
You can replace /photo with the URL path of the page you wish to redirect and /media with the new location. Of course, don’t fail to capitalize the first letter in Redirect.
Redirecting to External Pages
If you wish to redirect a page to an external destination, add this sample code to the .htaccess file of the domain you want to redirect visitors from –
Redirect 301 “/photo” “www.domain.com/new-location”
Redirecting Your Website to a New Domain
If you wish to redirect your website to a new domain, or a parked domain name to your main website, then use this code –
Redirect 301 “/” “www.yournewdomain.com/”
Besides URL redirects, you can also classify HTTPS and non-www redirects as permanent redirects.
Here are the sample redirect codes.
HTTP Redirection
As explained earlier, HTTPS redirection forces all visitors to connect securely, preventing hackers from exploiting the HTTP to attack the website.
You can force HTTPS connection on all pages for every visitor using this code at the beginning of the .htaccess file. –
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]
Non-WWW website to WWW URL Redirection
The www and non-www URLs of websites resolve to the same content, creating duplicates on the website.
For instance, a visitor accessing your website with the URL www.yourdomain.com and another using yourdomain.com will see the same content, and search engines don’t often take this lightly.
Now, imagine the number of duplicates that’ll sit on your website if it contains many pages.
But you can quickly resolve this by redirecting non-www URLs to their www versions, or vice versa.
Place this redirect rule in your .htaccess file to redirect from non-www to www.
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^yourdomain.com [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://www.yourdomain.com/$1 [L,R=301]
If you already have the RewriteEngine On line somewhere on the file, then use this code
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^yourdomain.com [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://www.yourdomain.com/$1 [L,R=301]
If you wish to redirect from www to non-www, then use this code.
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^yourdomain.com [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://yourdomain.com/$1 [L,R=301]
Ensure to remove the RewriteEngine On line from the code if it’s already on the file, and replace yourdomain.com with your domain name.
Temporary Redirect Code
You can use this sample code to redirect a page to a new location temporarily. Then, proceed.
Redirect 302 /photo /new-location
To temporarily redirect an entire website, then place this rule on your .htaccess file.
Redirect 301 /photo www.domain.com
Of course, don’t forget to replace www.domain.com with your domain name.
Creating Web Direct Via SPanel
You can set up web direct on SPanel via the file manager. If you’ve your code, then take these steps to get it done.
Step 1: Log Into SPanel’s User Interface
The default login URL is https://yourdomain.com/spanel (don’t forget to replace yourdomain.com with your actual domain).
Step 2: Go to Redirects
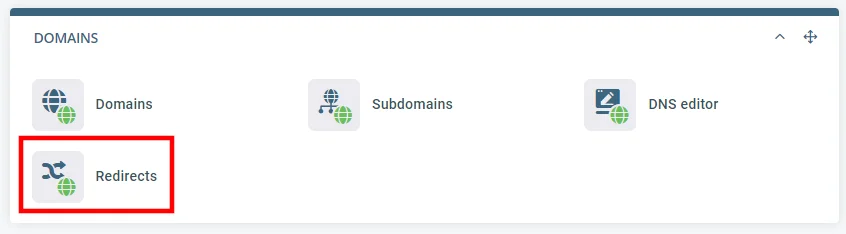
Under the Domains section on the homepage, you will see the Redirects tool.
Step 3: Enter the Redirect’s Parameters
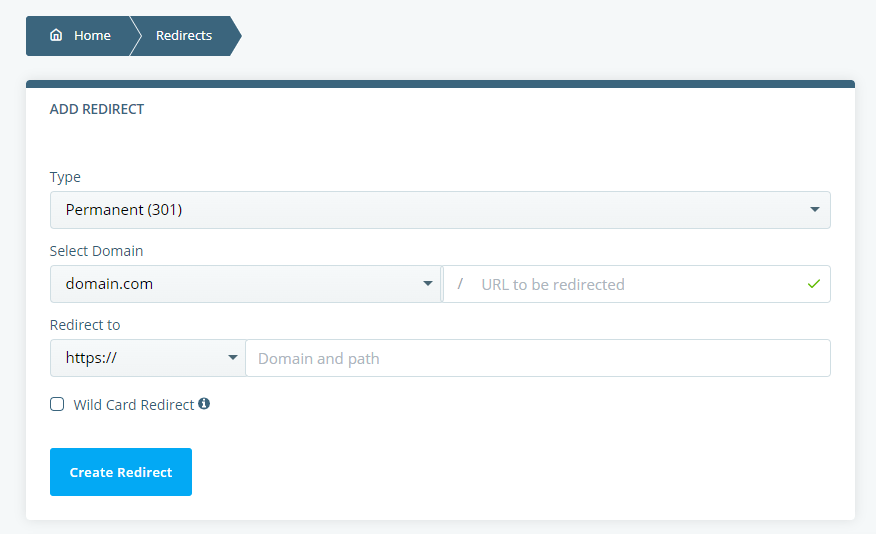
You need to choose the Type redirection and then enter the source and destination URLs. The Wild Card Redirect checkbox will instruct browsers to look for the files of the same name in the destination directory as well.
Web Direct Best Practices
Follow these best practices to set up your web redirect:
- Always redirect to a page that has matching content. For example, don’t redirect a page that talks about laptops to a mobile phone page. Instead, you could redirect to a top-level category, like Electronics.
- Avoid creating a redirect chain—that’s, redirecting to a page that redirects to another page, for example, A > B > C.
- When setting up www and non-www redirects, ensure to point it to the version you used as the canonical URL. For example, if your canonical URL is on www, redirect all non-www URLs to your www website—redirecting to the canonical URL fixes all potential duplication issues.
Need Support?
We understand setting up web redirects on your website could be challenging. So, if you need assistance creating one, kindly contact our support for quick help, and we’ll be available to help.