You could route your emails through our mail server even with your domain hosted elsewhere. It only requires buying a hosting plan and pointing your MX records to our mail server.
Companies relying heavily on emails for businesses might use two or more mail servers from different providers to ensure a server failure or downtime doesn’t prevent them from receiving essential communication.
They could use MX records to default to a second server when the primary server fails. Some might want to balance the email loads between servers to ensure the primary server doesn’t get overwhelmed and default to a third server when the servers fail.
This article guides you on using email with domains hosted elsewhere, but before we get to this, we first need to get a better understanding of some of the basic principles behind email delivery.
What’s MX Record?
MX record, short for mail exchanger record, is a DNS record that directs an email to a mail server. Pointing the record to your mail provider ensures you receive emails.
The records specify and prioritize the incoming mail servers that receive the email messages people send to your business email account.
Suppose you host your website with ScalaHosting but have your email handled by another provider. Your domain will be pointed to our nameservers, but the MX record will redirect email communication to the server handling your mails.
And, you could even use the two servers.
Understanding the MX Records Priority
MX priority value indicates your server preference.
With two servers, you have redundancy and can minimize the risk of email loss. It’s up to the MX records to assign priority values to them and configure the order the servers receive your email message.
You could use any number as the priority value.
The outgoing mail (SMTP) servers treat the record with the lowest number as the primary server and only delivers to the server with a higher priority value when the primary server fails, hence acting as a backup mail server.
For instance, if you use “10” as mail1.example.com MX record’s priority value and “20” for mail2.example.com, SMTP servers try mail1 first to deliver your emails before defaulting to mail2 when it fails.
But if you assign the value “10” to the two MX records and “20” to a third server, the email provider balances the load between mail1 and mail2 to avoid overwhelming the servers and defaults to mail3 when the servers fail.

This MX configuration balances the load but doesn’t specify any backup server, and you could lose your emails if the two servers fail. If you have a third server, assigning a higher priority value (like 20) specifies it as the backup.
Your emails default to that server when the ‘balancing’ servers fail. These fail-safe measures ensure you don’t lose important messages. The backup server receives your emails until the primary server(s) are back online.
Querying an MX Record
Message Transfer Agents (MTA) is a program for transporting, delivering, and forwarding mails, and you could liken it to an SMTP server. It queries your MX records to help you receive your email messages.
Let’s quickly examine how it works querying MX records? When people send you email messages, the MTA sends a DNS query to find the incoming mail servers that’ll receive the messages to establish an SMTP connection to those servers.
It tries to connect first to the most prioritized server (the domain with the lowest priority value).
If the primary server fails to handle the requests, the MTA defaults to the backup server, if specified, and reverts to the primary server when it comes back online.
But if there’s no backup server, email sending fails whenever the primary server goes down.
Adding MX Record to Your DNS Record
Follow these steps to add an MX record to your domain’s DNS zone.
Open your browser and log into SPanel’s User Interface.
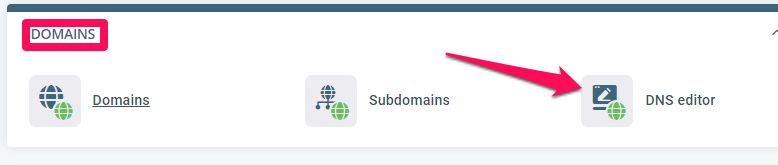
Scroll down the dashboard till you get to the DOMAINS section. Click the DNS editor tool to add an MX record to the domain.
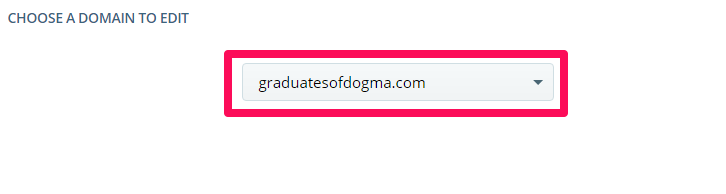
Select the domain you want to edit from the drop-domain menu.
Scroll to the ADD A NEW RECORD section and input your MX records information.
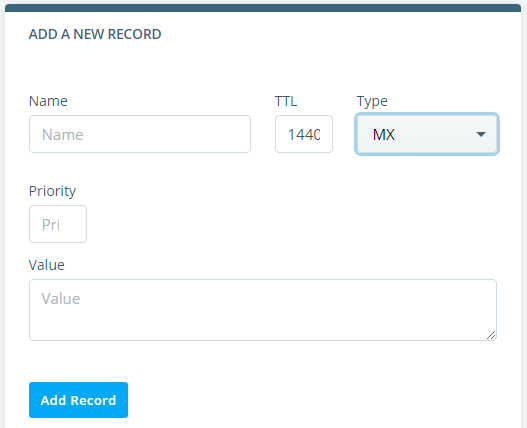
After that you need to :
- Enter your domain name (for instance, domain.com) in the Name field.
- Leave the default value in the TTL text box.
- Select MX as the DNS Type.
- Enter a value in the Priority text box.
- Type your mail server address in the Value text box. Use a Fully Qualified Domain Name like mail.domain.com instead of an IP address.
Click Add Record to add the MX configuration to your DNS records.
Repeat the steps to add another MX record for other mail servers. Use the same priority value to specify a ‘balancing’ server (if you want to balance the email loads) or a higher value for a backup mail server.
Wait for about 48 hours for the records to propagate across the internet, and you could use a free DNS Checker to monitor the propagation.
Editing MX Records
To edit your MX records in SPanel, log into the User Interface and open the DNS editor.
Scroll down to the list of existing DNS records, locate the MX record you want to edit, and click the Edit button.
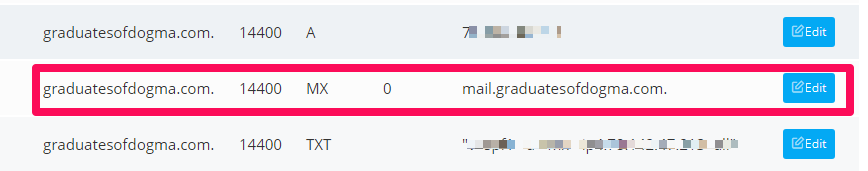
Make your changes on the dialogue box, click Save to enable the changes, or use the Delete button to remove the record from your DNS.
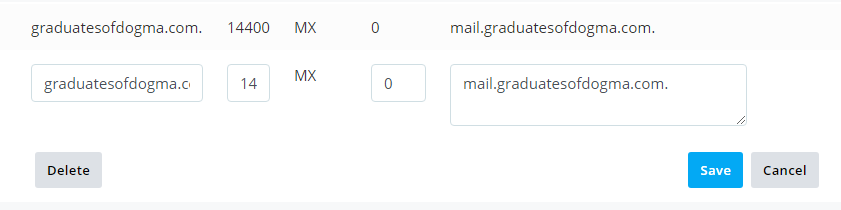
That’s it.
Wrapping It Up
You could prepare for mail server failures by configuring an MX record to point to a backup server, and this article makes adding MX records to your domain painless.
Follow the steps to set up this configuration in your SPanel in a few minutes, and don’t hesitate to contact support when you need assistance.
You could host your email servers on ScalaHosting for top-level performance, security, and scalability.
How To Point a Domain Name To a Web Hosting Provider

