There’s no point in having a website laden with information that users can’t access. While this may happen due to several factors like poor network or DNS failure, a faulty CDN could also be a problem.
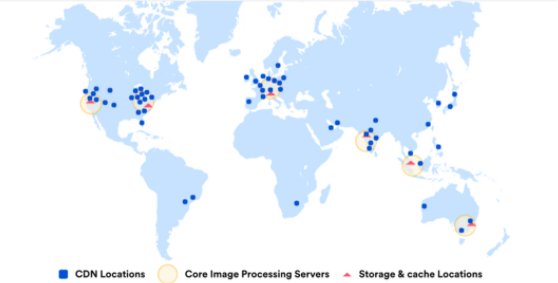
CDN stands for Content Delivery Network. It stores static contents (images, JavaScript, and CSS files) within its network and delivers them swiftly to users from all over the globe.
More than 400,000 websites out of 1,000,000 top websites globally store their website content in a CDN. It reduces website loading speed and prevents traffic spike issues by using many proxy servers in different parts of the world.
For instance, when you search for information online, CDNs use your closest server to create the connection. CDNs also store dynamic website contents and protect against potential site crashes.
Now, let’s take an in-depth look at the Content Delivery Network and why you should store your web content on it.
How Does a CDN Work?
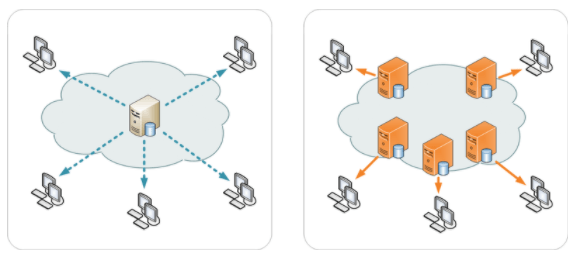
Image credit: Wikimedia Commons
A lot happens when people try to visit your site online. On one hand, the DNS servers try to sync your domain name with a matching IP address to bring up a web page. On the other hand, CDN servers accelerate the delivery of your static content saved on their servers. That way, your web visitors get a smooth user experience.
Let’s break it down further.
Say you type www.scalahosting.com on your browser. The computer sends a request that passes through several servers and routers to reach Scala Hosting’s server.
Now, Scala Hosting’s server is in the US. For example, if you stay in New Zealand, that would mean you’re requesting to access content from a server in the US.
A CDN server delivers parts of scalahosting.com from various locations closest to you, thereby reducing the distance between you and the web server. The closer your device gets to the server, the faster you get your results.
CDN servers have two essential components known as the Points Of Presence (POP) and Edge Servers. These servers route web traffic, mitigate attacks and increase loading speed.
They’re at populated locations around the globe to establish efficient networks.
So if your website has got CDN features, your content will be on multiple CDN servers through a process called caching. Each time a user accesses your site, a CDN server retrieves cached content from your origin server.
What is a CDN Point of Presence (POP)?
The Point of Presence (POP) plays an essential role in a Content Delivery Network. It refers to the physical data centers positioned at many locations. These data centers enable online users to content nearest to them.
For instance, a London visitor requesting to view content from a US-based server may encounter a slow loading issue. But, using a local UK server (POP) can hasten the loading speed.
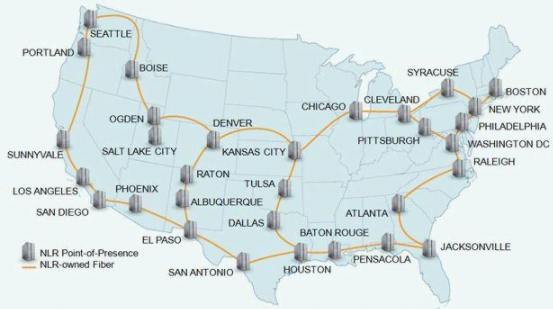
Image credit: Sam Churchill via Flickr
The CDN keeps a cached form of your site contents at various physical locations. These locations are called Points of Presence (POP).
The whole point of this is to direct a user’s request to the closest POP, such that when they request content from a site, the nearest POP receives it and delivers the content.
Contents here expand beyond web content only. It also includes audio streams, OS updates, games, apps, HD, and 4K videos.
The POP has its caching servers responsible for providing content in the user area. It comprises one or more edge servers positioned at Internet Exchange Points (IXP). Internet Service Providers (ISPs) use these data centers to interlink their networks.
What are CDN Edge Servers?
Like POPs, Edge servers are also responsible for making content more accessible to users through edge computing.
CDN edge servers function in moving data exchange points from a busy central location to the network edge and then nearer to end-users.
The end-point users own devices that let them instantly consume the content.
This could be:
- mobile phones
- laptops
- personal computers
- other devices
Unlike the POP-single servers in one area, edge servers are located in scanty new Internet Exchange Points (IXPs).
Edge servers allow the use of defensive techniques near the end-user. Thus, they provide tight network security.
Why Do You Need a CDN?
As mentioned, CDNs offer blazing fast website speed while lowering latency.
Though it provides a superior user experience for your site visitors, the truth is, if most of your users are in one area, the benefits will be negligible.
That aside, you’ll need a CDN for various reasons.
These reasons may include:
- The inability to provide quick internet service
- Providing diverse content types to your audience
- Device detection, and
- Data security
CDN curbs situations like these by providing fast loading speed and website stability. Asides from this, there are several other reasons why you should consider a CDN for your website.
We’ll talk about them in a few.
To Improve User Experience
If you have a global audience, a CDN will cache static resources on edge servers nearer to your users. It is perfect for website owners creating images and intensive bandwidth video content.
The page loading speed of your site will deliver content faster and improve users’ experience.
To Increase Speed and Reduce Latency
A two-second load time may not be feasible for your website, but five seconds can cost you 38 percent of your customers. CDNs reduce website average loading speed by shortening the distance between the servers and users. Fast websites also enhance user experience and Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
For Efficient and Secure Delivery of Content
Using the Content Delivery Network (CDN) secures your WordPress site. It prevents an attack from the Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS). Thus blocks harmful requests from affecting your database.
Also, a few CDNs provide extra firewall protection and two-factor authentication. Another option to use is its Bot filtering feature.
For Site Stability During Traffic Spikes
If you don’t enable CDN features on your website, you might experience a sudden surge in traffic, making it crash or become inaccessible to users.
Your hosting provider and pricing plan may also contribute to this.
How?
Subscribing to a smaller plan limits your user visits and other features. So, when your website attracts a higher traffic number than your hosting plan, it crashes.
A CDN allows you to reduce this risk by sharing the load to many servers. This guarantees a smooth and stable website.
Rounding Up
Content Delivery Networks (CDN) allow reliable, stable, and efficient delivery of website content.
We recommend storing your website content in a CDN, especially if you are running a long-term profitable business. This requires you to choose a suitable hosting plan with a reliable hosting provider.
Scala Hosting offers free CDN services, alongside free SSL and unlimited bandwidth to cater to all your hosting needs.
